| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Hydrogen bonds are formed between a species with a polar X δ - -H δ + bond and a species with a lone pair (Y δ - ), i.e., X δ - -H δ +... Y δ - . The most common species for X are oxygen and nitrogen, and to a lesser extent carbon, fluorine, and sulfur. However, as long as the X-H bond is polar then hydrogen bonding is possible. Similarly, the most common Lewis bases that hydrogen bond involve oxygen, nitrogen, and fluorine as the donor atom. Again there are many examples of other atoms, but as long as the atom has a lone pair that is chemically active, hydrogen bonding can occur.
The majority of hydrogen bonds are asymmetrical, that is the hydrogen is closer to one atom than the other ( [link] ), even when X and Y are the same element, i.e., O-H ... O. While the typical hydrogen bond involves one Lewis base (lone pair donor), there are many examples where the hydrogen interacts with two Lewis base lone pairs ( [link] ).
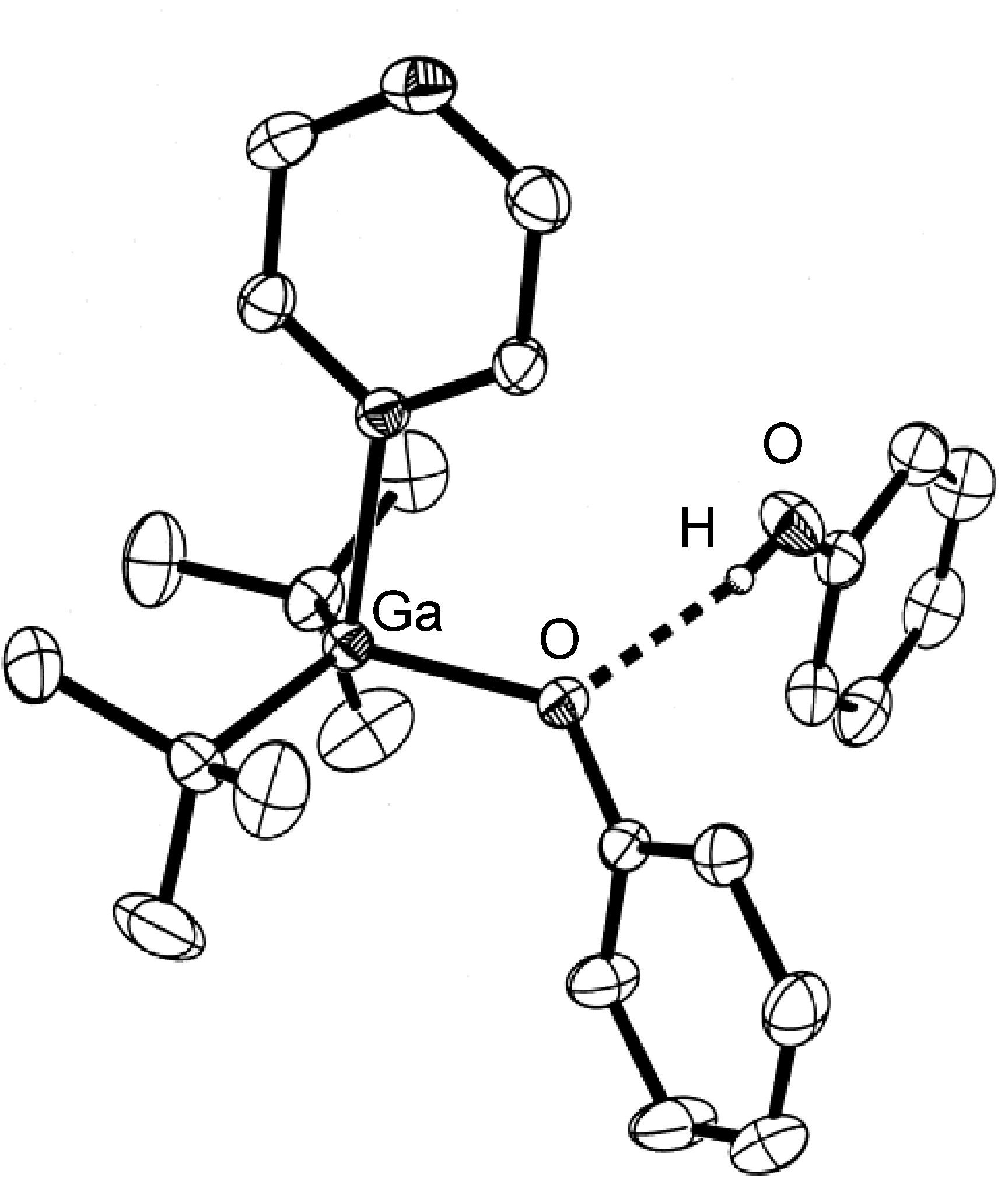
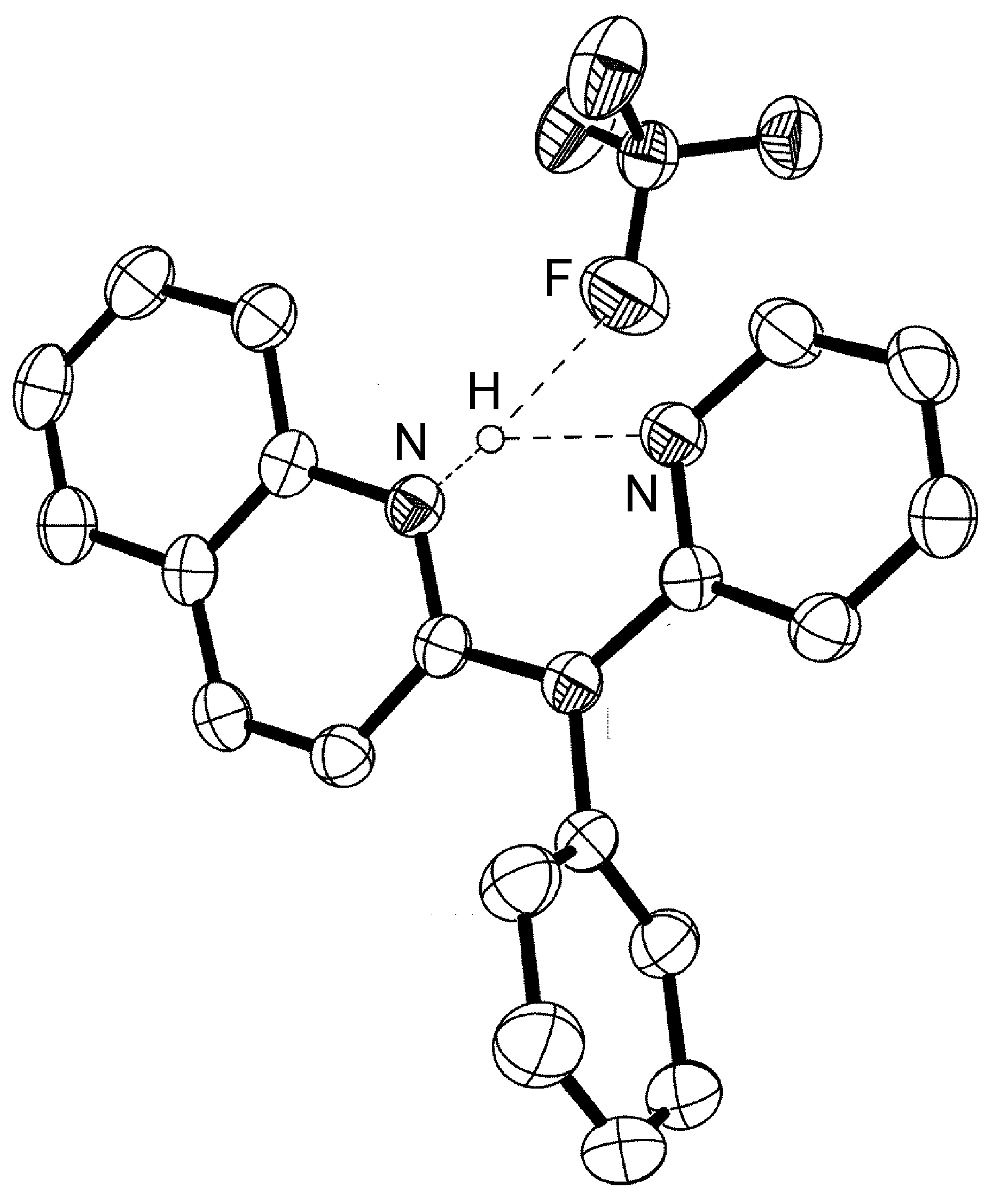
Hydrogen bonds are mostly electrostatic attractions, and as such they are weaker than covalent bonds, but stronger than van der Waal interactions. With bond strengths generally covering the range of 5 – 50 kJ/mol, the energy required to break a hydrogen bond is comparable to that of thermal motion within the temperature range of 0 – 200 °C. As a consequence the number of groups involved in hydrogen bonding decreases with increasing temperature, until few hydrogen bonds are observed in the vapor phase. One noted exception is the hydrogen bridged anion [F-H-F] - , in which the strong interaction (243 kJ/mol) is covalent in character involving a three-center molecular orbital bond.
Although hydrogen bonds may be characterized with respect to the X and Y atom, it is more useful to classify them as either intramolecular or intermolecular hydrogen bonds. This is due to the difference in physical and chemical properties between these two classes.
Intramolecular hydrogen bonds (X-H ... Y) arise where the X and Y atoms are in the same molecule ( [link] ).
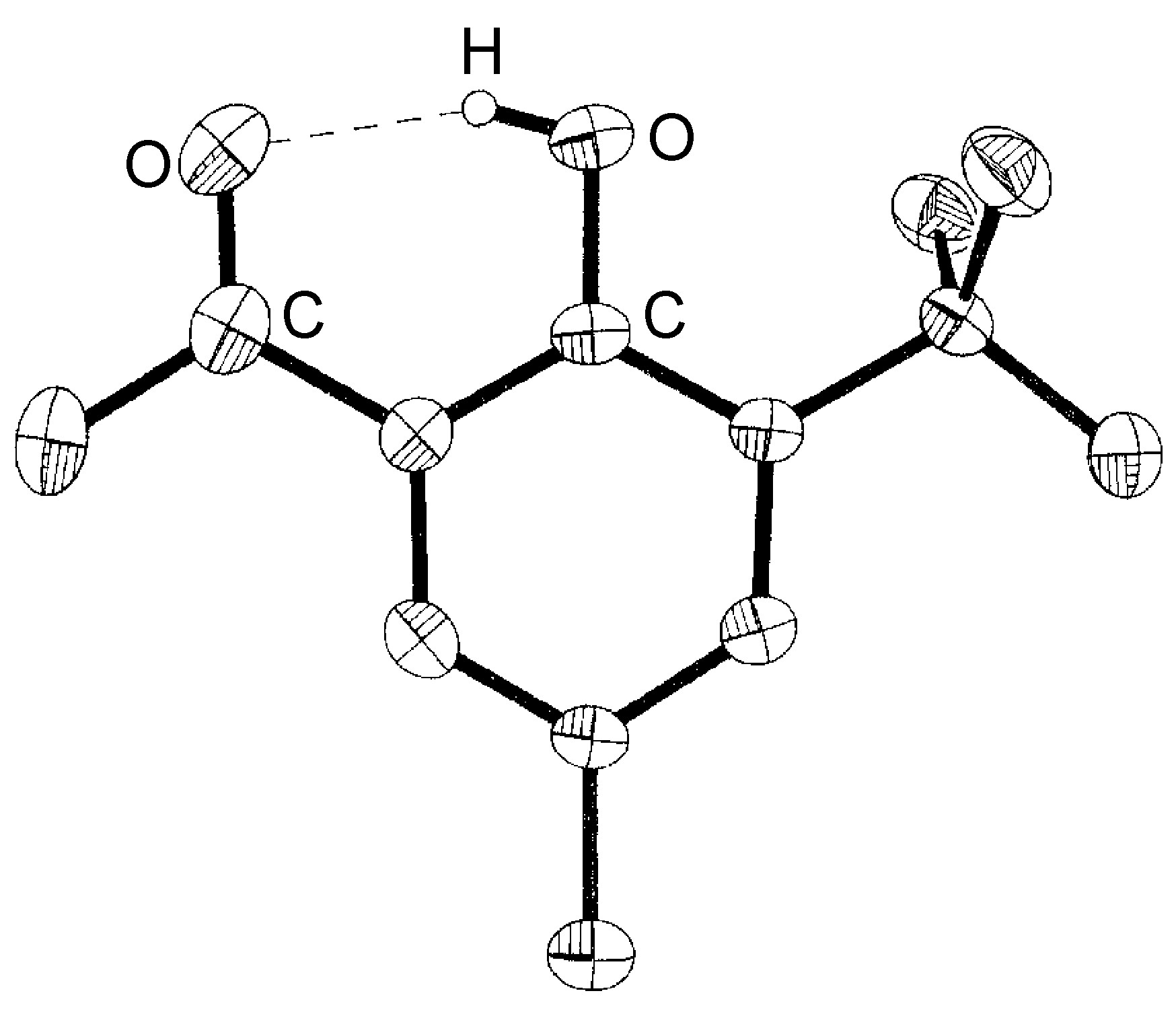
If the hydrogen bond (X-H ... Y) involves X and Y being from different molecules this is an intermolecular hydrogen bond. Within the range of intermolecular hydrogen bonded compounds there are two sub-categories: those involving discrete molecular species (oligomers) and those resulting in polymeric species.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Hydrogen' conversation and receive update notifications?