| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
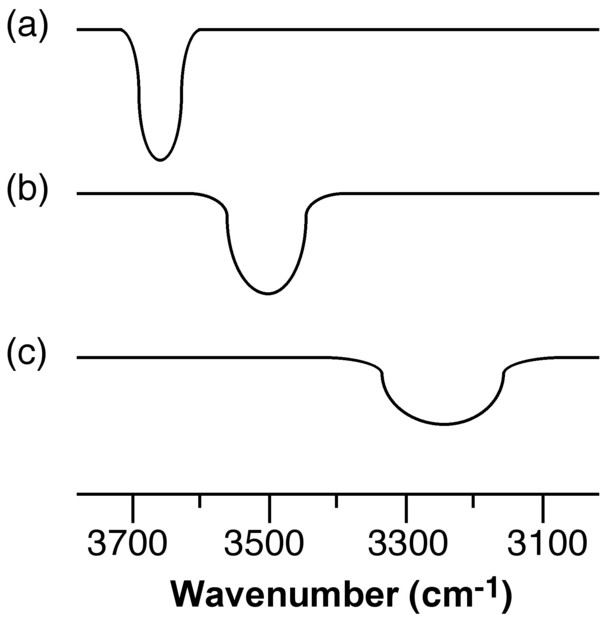
The X-H stretching frequency in the IR (and Raman) spectrum is dependant on the identity of X, i.e., O-H = 3610 - 3640 cm -1 and N-H = 3400 - 3500 cm -1 . However, the ν(X-H) is shifted to lower energy (lower frequency) as a consequence of hydrogen bonding. In addition, while non-hydrogen bonded X-H stretches are sharp, the presence of hydrogen bonding results in the peak being broadened. Figure X demonstrates both these effects. The O-H stretch for dilute n BuOH in CCl 4 is a sharp peak at 3650 cm -1 due to the lack of hydrogen bonding between the two components ( [link] a), and the presence of hydrogen bonding between n BuOH and n BuOH is limited by the dilution. By contrast, a dilute solution of n BuOH in Et 2 O results in a shift to lower frequency and a significant increase of peak width ( [link] b) as a result of fairly strong O-H ... O bonds. Finally, a dilute solution of n BuOH in NMe 3 results in a further shift to 3250 cm -1 and a very broad peak ( [link] c). The broadening of the peaks is due to the distribution of X-H distances within a X-H ... Y hydrogen bond.
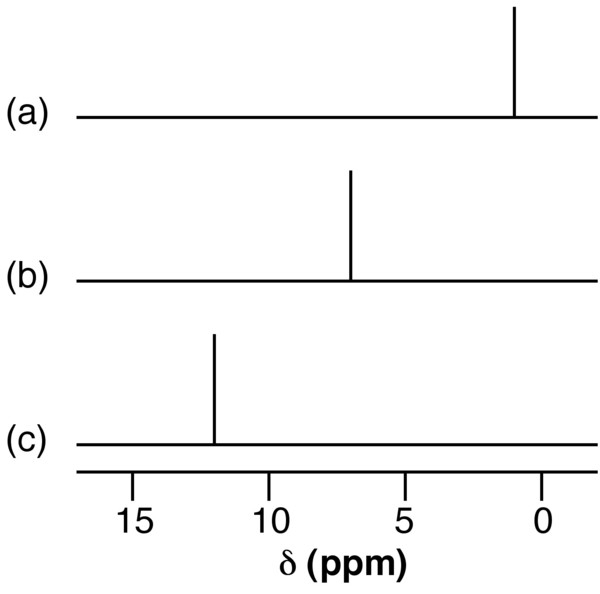
The presence of hydrogen bonding results the shift to higher ppm (lower frequency) of the 1 H NMR resonance for the proton. This shift is due to the decrease in shielding of the proton. A dilute solution of n BuOH in CCl 4 shows a resonance typical of a non-hydrogen bonded compound ( [link] a), while that for n BuOH in NMe 3 ( [link] b) shows a significant low field shift. Very strong intra or intermolecular hydrogen bonded species show a very large 1 H NMR shift (e.g., [link] c).
The presence of intermolecular hydrogen bonding provides additional attractive forces between molecules. Thus, properties that depend on intramolecular forces are affected.
Liquids with significant hydrogen bonding exhibit higher boiling points, higher viscosity, and higher heat of vaporization (ΔH v ) as compared to analogous compounds without extensive hydrogen bonding. For solids the presence of hydrogen bonding results in an increase in the melting point of the solid and an increase in the associated heat of fusion (ΔH f ).
The archetypal case for the effect of hydrogen bonding is the melting and boiling points of the hydrides of the Group 16 elements, i.e., H 2 E. For a series of analogous compounds with the same molecular structure it would be expected that the boiling points would be related to the molecular mass. However, as can be seen from [link] , the melting and boiling points of water are anomalously higher than those of its heavier analogs. In fact from [link] it is clear that just considering H 2 S, H 2 Se, and H 2 Te, the expected trend is observed, and it is similar to that for the Group 14 hydrides (CH 4 , SiH 4 , etc). Therefore, water must have additional intermolecular forces as compared to its heavier homologs. This observation is consistent with the strong hydrogen bonding in water, and the very weak if nonexistent hydrogen bonding in the sulfur, selenium, and tellurium analogs.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Hydrogen' conversation and receive update notifications?