| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Liquid crystals are a state of matter that has the properties between solid crystal and common liquid. There are basically three different types of liquid crystal phases:
Thermotropic LCs are the most widely used one, which can be divided into five categories:
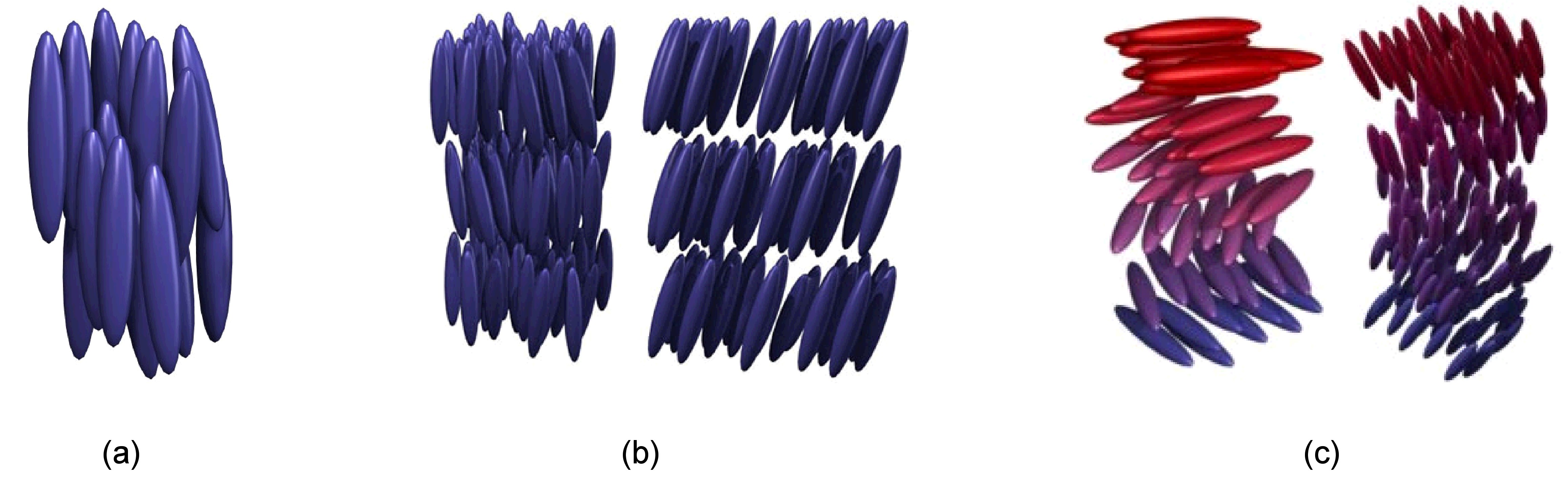
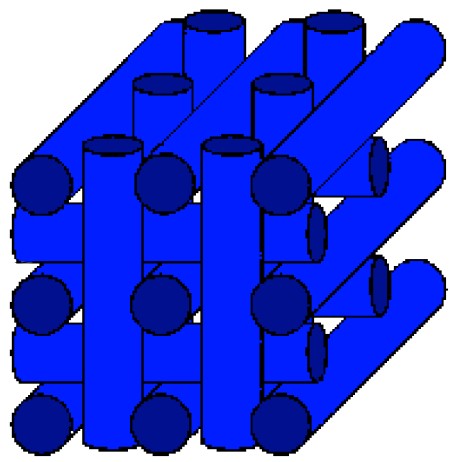

Thermotropic LCs are very sensitive to temperature. If the temperature is too high, thermal motion will destroy the ordering of LCs, and push it into a liquid phase. If the temperature is too low, thermal motion is hard to perform, so the material will become crystal phase.
The existence of liquid crystal phase can be detected by using polarized optical microscopy, since liquid crystal phase exhibits its unique texture under microscopy. The contrasting areas in the texture correspond to domains where LCs are oriented towards different directions.
Polarized optical microscopy is typically used to detect the existence of liquid crystal phases in a solution. The principle of this is corresponding to the polarization of light. A polarizer is a filter that only permits the light oriented in a specific direction with its polarizing direction to pass through. There are two polarizers in a polarizing optical microscope (POM) ( [link] ) and they are designed to be oriented at right angle to each other, which is termed as cross polar. The fundamental of cross polar is illustrated in [link] , the polarizing direction of the first polarizer is oriented vertically to the incident beam, so only the waves with vertical direction can pass through it. The passed wave is subsequently blocked by the second polarizer, since this polarizer is oriented horizontally to the incident wave.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?