| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Though the signal’s position is well-defined according to the position of the xy mirrors, the signal from fluorescence is relatively weak after passing through the pinhole, so a photomultiplier tube is used to detect emitted photons. Detecting all photons without regard to spatial position increases the signal, and the photomultiplier tube further increases the detection signal by propagating an electron cascade resulting from the photoelectric effect (incident photons kicking off electrons). The resulting signal is an analog electrical signal with continuously varying voltage that corresponds to the emission intensity. This is periodically sampled by an analog-to-digital converter.
It is important to understand that the image is a reconstruction of many points sampled across the specimen. At any given time the microscope is only looking at a tiny point, and no complete image exists that can be viewed at an instantaneous point in time. Software is used to recombine these points to form an image plane, and combine image planes to form a 3-D representation of the sample volume.
Two-photon microscopy is a technique whereby two beams of lower intensity are directed to intersect at the focal point. Two photons can excite a fluorophore if they hit it at the same time, but alone they do not have enough energy to excite any molecules. The probability of two photons hitting a fluorophore at nearly the exact same time (less than 10 -16 ) is very low, but more likely at the focal point. This creates a bright point of light in the sample without the usual cone of light above and below the focal plane, since there are almost no excitations away from the focal point.

To increase the chance of absorption, an ultra-fast pulsed laser is used to create quick, intense light pulses. Since the hourglass shape is replaced by a point source, the pinhole near the detector (used to reduce the signal from light originating from outside the focal plane) can be eliminated. This also increases the signal-to-noise ratio (here is very little noise now that the light source is so focused, but the signal is also small). These lasers have lower average incident power than normal lasers, which helps reduce damage to the surrounding specimen. This technique can image deeper into the specimen (~400 μm), but these lasers are still very expensive, difficult to set up, require a stronger power supply, intensive cooling, and must be aligned in the same optical table because pulses can be distorted in optical fibers.
Confocal microscopy is very useful for determining the relative positions of particles in three dimensions [link] . Software allows measurement of distances in the 3D reconstructions so that information about spacing can be ascertained (such as packing density, porosity, long range order or alignment, etc.).
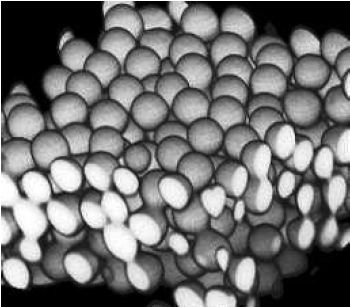
If imaging in fluorescence mode, remember that the signal will only represent the locations of the individual fluorophores. There is no guarantee fluorophores will completely attach to the structures of interest or that there will not be stray fluorophores away from those structures. For microparticles it is often possible to attach the fluorophores to the shell of the particle, creating hollow spheres of fluorophores. It is possible to tell if a sample sphere is hollow or solid but it would depend on the transparency of the material.
Dispersions of microparticles have been used to study nucleation and crystal growth, since colloids are much larger than atoms and can be imaged in real-time. Crystalline regions are determined from the order of spheres arranged in a lattice, and regions can be distinguished from one another by noting lattice defects.
Self-assembly is another application where time-dependent, 3-D studies can help elucidate the assembly process and determine the position of various structures or materials. Because confocal is popular for biological specimens, the position of nanoparticles such as quantum dots in a cell or tissue can be observed. This can be useful for determining toxicity, drug-delivery effectiveness, diffusion limitations, etc.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?