| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
[link] shows a chromatogram of the analysis of residual methanol in biodiesel, which is one of the required properties that must be measured to ensure the quality of the product at the time and place of delivery.
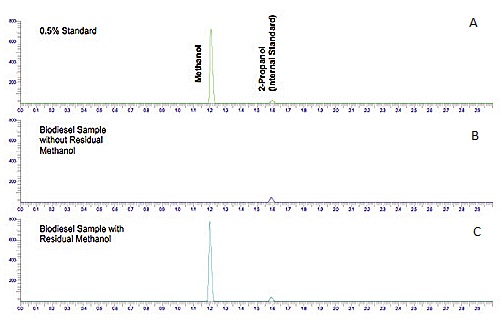
Chromatogram ( [link] a) shows a standard solution of methanol with 2-propanol as the internal standard. From the figure it can be seen that methanol has a higher affinity for the mobile phase (lower K c ) than 2-propanol (iso-propanol), and therefore elutes first. Chromatograms ( [link] b and c) show two samples of biodiesel, one with methanol ( [link] b) and another with no methanol detection. The internal standard was added to both samples for quantitation purposes.
[link] shows a schematic diagram of the components of a typical gas chromatograph, while [link] shows a photograph of a typical gas chromatograph coupled to a mass spectrometer (GC/MS).
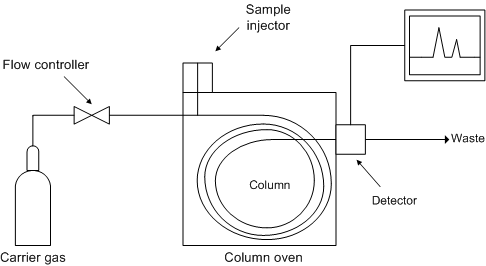

The role of the carrier gas -GC mobile phase- is to carry the sample molecules along the column while they are not dissolved in or adsorbed on the stationary phase. The carrier gas is inert and does not interact with the sample, and thus GC separation's selectivity can be attributed to the stationary phase alone. However, the choice of carrier gas is important to maintain high efficiency. The effect of different carrier gases on column efficiency is represented by the van Deemter (packed columns) and the Golay equation (capillary columns). The van Deemter equation, [link] , describes the three main effects that contribute to band broadening in packed columns and, as a consequence, to a reduced efficiency in the separation process.
These three factors are:
The broadening is described in terms of the height equivalent to a theoretical plate, HEPT, as a function of the average linear gas velocity, u . A small HEPT value indicates a narrow peak and a higher efficiency.
Since capillary columns do not have any packing, the Golay equation, [link] , does not have an A-term. The Golay equation has 2 C-terms, one for mass transfer in then stationary phase (C s ) and one for mass transfer in the mobile phase (C M ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?