| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
All liquids have a natural internal resistance to flow termed viscosity. Viscosity is the result of frictional interactions within a given liquid and is commonly expressed in two different ways.
The first is dynamic viscosity, also known as absolute viscosity, which measures a fluid’s resistance to flow. In precise terms, dynamic viscosity is the tangential force per unit area necessary to move one plane past another at unit velocity at unit distance apart. As one plane moves past another in a fluid, a velocity gradient is established between the two layers ( [link] ). Viscosity can be thought of as a drag coefficient proportional to this gradient.
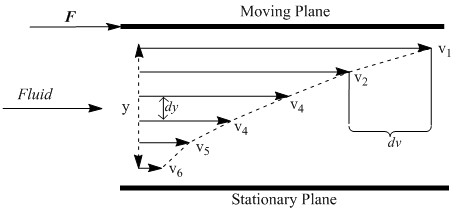
The force necessary to move a plane of area A past another in a fluid is given by [link] where V is the velocity of the liquid, Y is the separation between planes, and η is the dynamic viscosity.
V/Y also represents the velocity gradient (sometimes referred to as shear rate). Force over area is equal to τ, the shear stress, so the equation simplifies to [link] .
For situations where V does not vary linearly with the separation between plates, the differential formula based on Newton’s equations is given in [link] .
Kinematic viscosity, the other type of viscosity, requires knowledge of the density, ρ, and is given by [link] , where ν is the kinematic viscosity and η is the dynamic viscosity.
Viscosity is commonly expressed in Stokes, Poise, Saybolt Universal Seconds, degree Engler, and SI units.
The SI units for dynamic (absolute) viscosity is given in units of N·S/m 2 , Pa·S, or kg/(m·s), where N stands for Newton and Pa for Pascal. Poise are metric units expressed as dyne·s/cm 2 or g/(m·s). They are related to the SI unit by g/(m·s) = 1/10 Pa·S. 100 centipoise, the centipoise (cP) being the most used unit of viscosity, is equal to one Poise.
[link] shows the interconversion factors for dynamic viscosity. [link] lists the dynamic viscosities of several liquids at various temperatures in centipoise. The effect of the temperature on viscosity is clearly evidenced in the drastic drop in viscosity of water as the temperature is increased from near ambient to 60 degrees Celsius. Ketchup has a viscosity of 1000 cP at 30 degrees Celsius or more than 1000 times that of water at the same temperature!
| Unit | Pa*S | dyne·s/cm 2 or g/(m·s) (Poise) | Centipoise (cP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pa*S | 1 | 10 | 1000 |
| dyne·s/cm 2 or g/(m·s) (Poise) | 0.1 | 1 | 100 |
| Centipoise (cP) | 0.001 | 0.01 | 1 |
| Liquid | η (cP) | Temperature(°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Water | 0.89 | 25 |
| Water | 0.47 | 60 |
| Milk | 2.0 | 18 |
| Olive Oil | 107.5 | 20 |
| Toothpaste | 70,000-100,000 | 18 |
| Ketchup | 1000 | 30 |
| Custard | 1,500 | 85-90 |
| Crude Oil (WTI)* | 7 | 15 |
The CGS unit for kinematic viscosity is the Stoke which is equal to 10 -4 m 2 /s. Dividing by 100 yields the more commonly used centistoke. The SI unit for viscosity is m 2 /s. The Saybolt Universal second is commonly used in the oilfield for petroleum products represents the time required to efflux 60 milliliters from a Saybolt Universal viscometer at a fixed temperature according to ASTM D-88. The Engler scale is often used in Britain and quantifies the viscosity of a given liquid in comparison to water in an Engler viscometer for 200cm 3 of each liquid at a set temperature.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?