| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
The information presented in this section supports the following AP® learning objectives and science practices:
We can represent electric potentials (voltages) pictorially, just as we drew pictures to illustrate electric fields. Of course, the two are related. Consider [link] , which shows an isolated positive point charge and its electric field lines. Electric field lines radiate out from a positive charge and terminate on negative charges. While we use blue arrows to represent the magnitude and direction of the electric field, we use green lines to represent places where the electric potential is constant. These are called equipotential lines in two dimensions, or equipotential surfaces in three dimensions. The term equipotential is also used as a noun, referring to an equipotential line or surface. The potential for a point charge is the same anywhere on an imaginary sphere of radius surrounding the charge. This is true since the potential for a point charge is given by and, thus, has the same value at any point that is a given distance from the charge. An equipotential sphere is a circle in the two-dimensional view of [link] . Since the electric field lines point radially away from the charge, they are perpendicular to the equipotential lines.
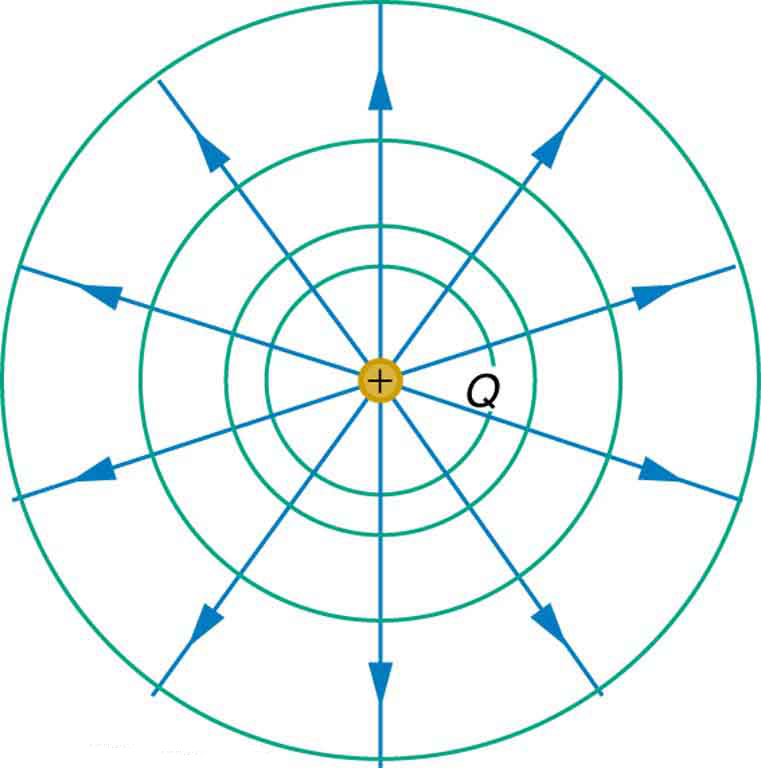
Starting with [link] as a rough example, draw diagrams of isolines for both positive and negative isolated point charges. Be sure to take care with what happens to the spacing of the isolines as you get closer to the charge. Then copy both of these sets of lines, but relabel them as gravitational equipotential lines. Then try to draw the sort of hill or hole or other shape that would have equipotential lines of this form. Does this shape exist in nature?
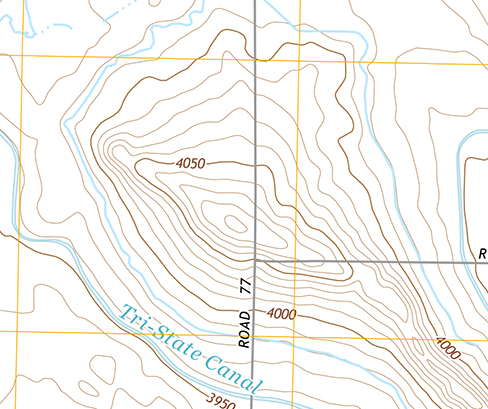
You should notice that the lines get closer together the closer you get to the point charge. The hill (or sinkhole, for the equivalent from a negative charge) should have a 1/ r sort of form, which is not a very common topographical feature.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?