| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAAT) are used in molecular biology to detect unique nucleic acid sequences of viruses in patient samples. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is an NAAT used to detect the presence of viral DNA in a patient’s tissue or body fluid sample. PCR is a technique that amplifies (i.e., synthesizes many copies) of a viral DNA segment of interest. Using PCR, short nucleotide sequences called primers bind to specific sequences of viral DNA, enabling identification of the virus.
Reverse transcriptase-PCR (RT-PCR) is an NAAT used to detect the presence of RNA viruses. RT-PCR differs from PCR in that the enzyme reverse transcriptase (RT) is used to make a cDNA from the small amount of viral RNA in the specimen. The cDNA can then be amplified by PCR. Both PCR and RT-PCR are used to detect and confirm the presence of the viral nucleic acid in patient specimens.
Michelle, a 21-year-old nursing student, came to the university clinic worried that she might have been exposed to a sexually transmitted disease (STD). Her sexual partner had recently developed several bumps on the base of his penis. He had put off going to the doctor, but Michelle suspects they are genital warts caused by HPV. She is especially concerned because she knows that HPV not only causes warts but is a prominent cause of cervical cancer. She and her partner always use condoms for contraception, but she is not confident that this precaution will protect her from HPV.
Michelle’s physician finds no physical signs of genital warts or any other STDs, but recommends that Michelle get a Pap smear along with an HPV test. The Pap smear will screen for abnormal cervical cells and the CPEs associated with HPV; the HPV test will test for the presence of the virus. If both tests are negative, Michelle can be more assured that she most likely has not become infected with HPV. However, her doctor suggests it might be wise for Michelle to get vaccinated against HPV to protect herself from possible future exposure.
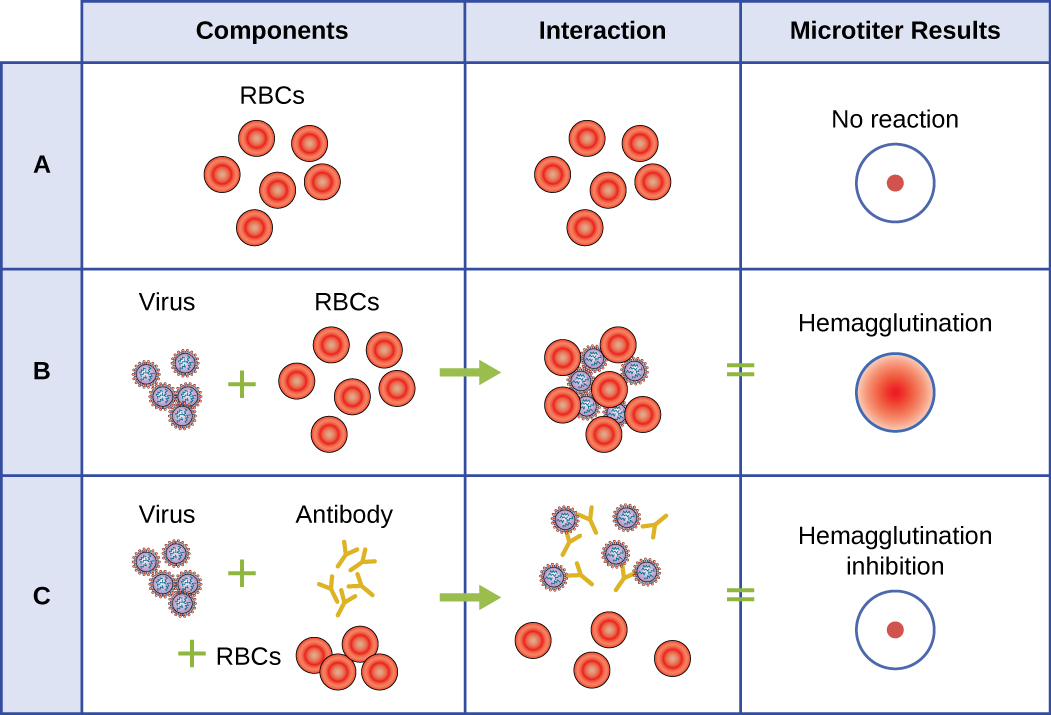
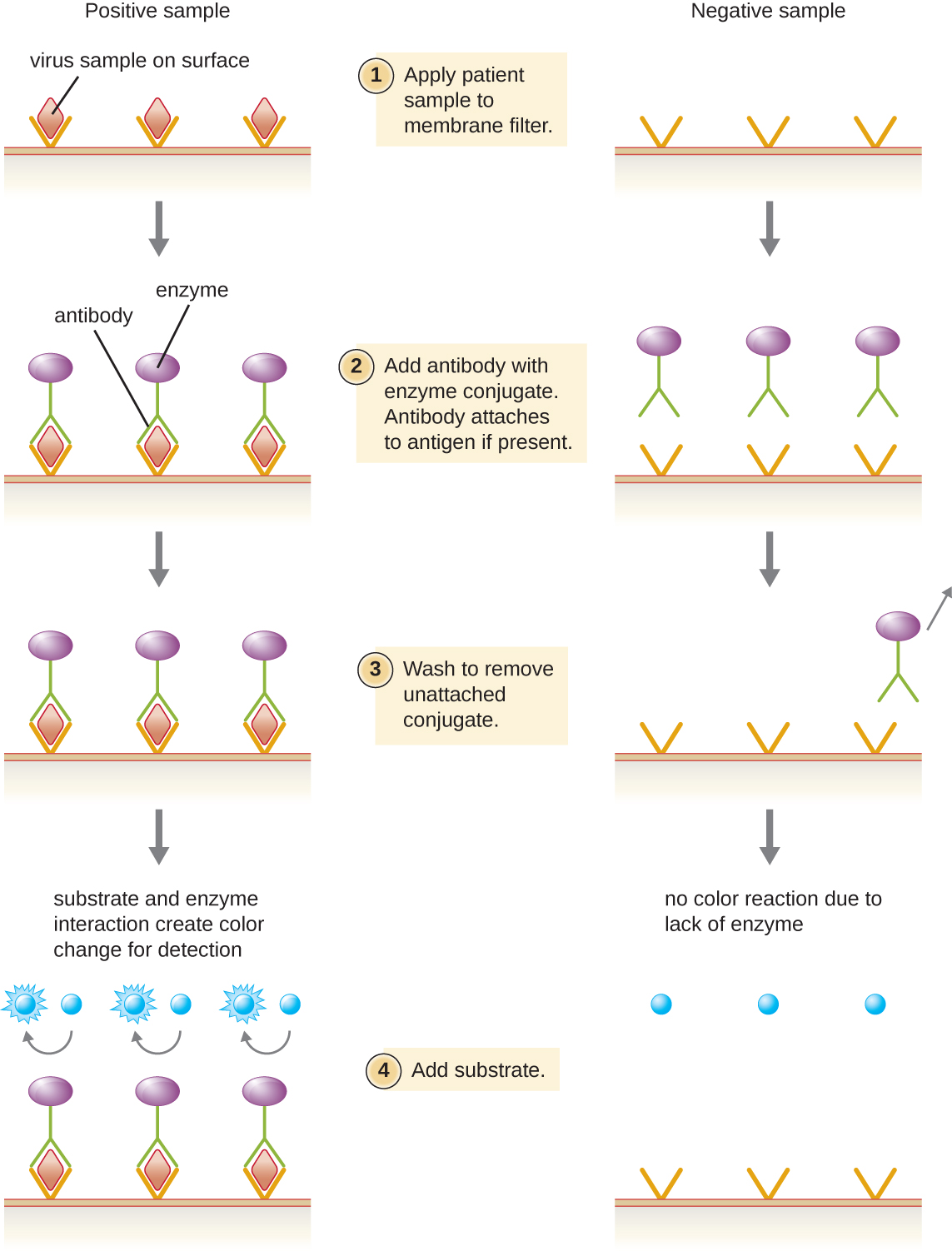
Enzyme immunoassays (EIAs) rely on the ability of antibodies to detect and attach to specific biomolecules called antigens. The detecting antibody attaches to the target antigen with a high degree of specificity in what might be a complex mixture of biomolecules. Also included in this type of assay is a colorless enzyme attached to the detecting antibody. The enzyme acts as a tag on the detecting antibody and can interact with a colorless substrate, leading to the production of a colored end product. EIAs often rely on layers of antibodies to capture and react with antigens, all of which are attached to a membrane filter (see [link] ). EIAs for viral antigens are often used as preliminary screening tests. If the results are positive, further confirmation will require tests with even greater sensitivity, such as a western blot or an NAAT . EIAs are discussed in more detail in EIAs and ELISAs .
Along with the RT/PCR analysis, David’s saliva was also collected for viral cultivation. In general, no single diagnostic test is sufficient for antemortem diagnosis, since the results will depend on the sensitivity of the assay, the quantity of virions present at the time of testing, and the timing of the assay, since release of virions in the saliva can vary. As it turns out, the result was negative for viral cultivation from the saliva. This is not surprising to David’s doctor, because one negative result is not an absolute indication of the absence of infection. It may be that the number of virions in the saliva is low at the time of sampling. It is not unusual to repeat the test at intervals to enhance the chance of detecting higher virus loads.
Jump to the next Clinical Focus box. Go back to the previous Clinical Focus box.
Viruses can be diagnosed and observed using a(n) _____________ microscope.
Electron
Cell abnormalities resulting from a viral infection are called ____________ _____________.
cytopathic effects
Briefly explain the various methods of culturing viruses.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?