| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

Although complete sterilization is ideal for many medical applications, it is not always practical for other applications and may also alter the quality of the product. Boiling and autoclaving are not ideal ways to control microbial growth in many foods because these methods may ruin the consistency and other organoleptic (sensory) qualities of the food. Pasteurization is a form of microbial control for food that uses heat but does not render the food sterile. Traditional pasteurization kills pathogens and reduces the number of spoilage-causing microbes while maintaining food quality. The process of pasteurization was first developed by Louis Pasteur in the 1860s as a method for preventing the spoilage of beer and wine. Today, pasteurization is most commonly used to kill heat-sensitive pathogens in milk and other food products (e.g., apple juice and honey) ( [link] ). However, because pasteurized food products are not sterile, they will eventually spoil.
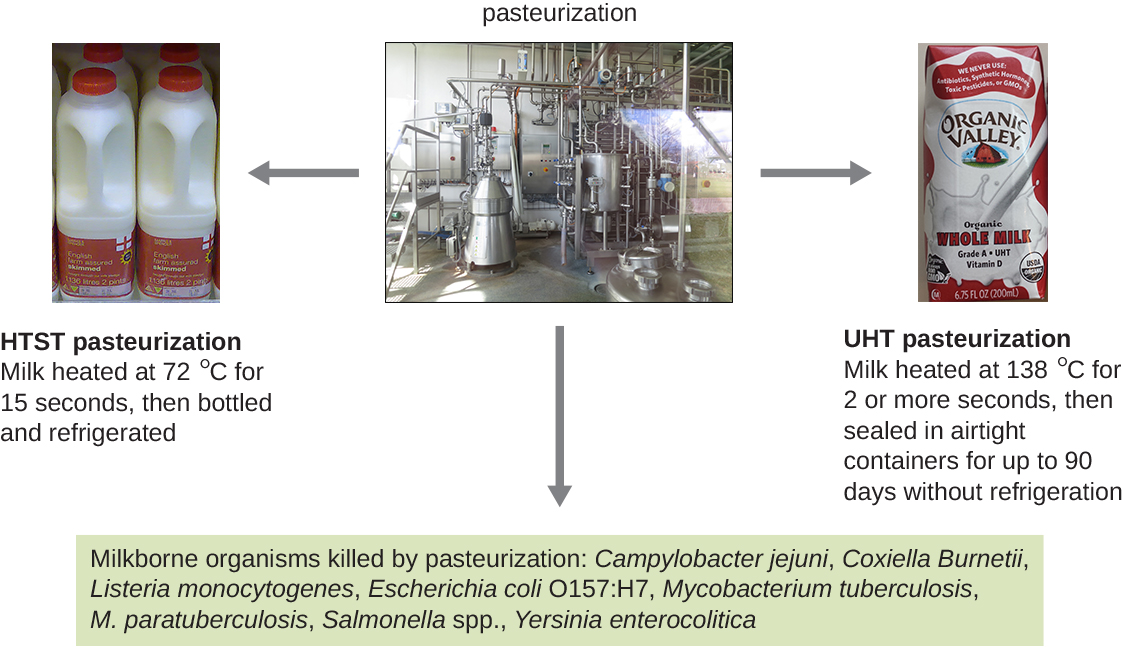
The methods used for milk pasteurization balance the temperature and the length of time of treatment. One method, high-temperature short-time (HTST) pasteurization , exposes milk to a temperature of 72 °C for 15 seconds, which lowers bacterial numbers while preserving the quality of the milk. An alternative is ultra-high-temperature (UHT) pasteurization , in which the milk is exposed to a temperature of 138 °C for 2 or more seconds. UHT pasteurized milk can be stored for a long time in sealed containers without being refrigerated; however, the very high temperatures alter the proteins in the milk, causing slight changes in the taste and smell. Still, this method of pasteurization is advantageous in regions where access to refrigeration is limited.
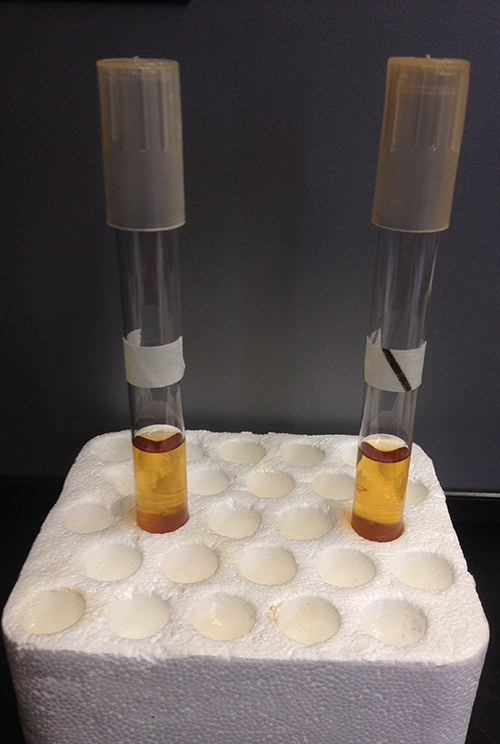
Just as high temperatures are effective for controlling microbial growth, exposing microbes to low temperatures can also be an easy and effective method of microbial control, with the exception of psychrophiles , which prefer cold temperatures (see Temperature and Microbial Growth ). Refrigerators used in home kitchens or in the laboratory maintain temperatures between 0 °C and 7 °C. This temperature range inhibits microbial metabolism, slowing the growth of microorganisms significantly and helping preserve refrigerated products such as foods or medical supplies. Certain types of laboratory cultures can be preserved by refrigeration for later use.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?