| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
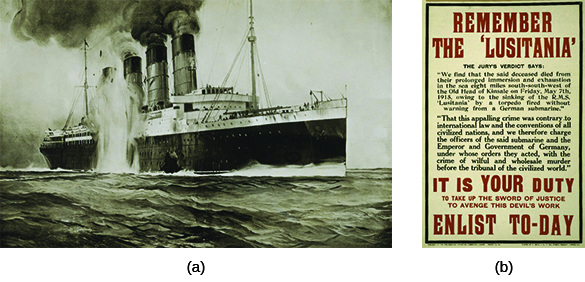
Despite the loss of American lives on the Lusitania , President Wilson stuck to his path of neutrality in Europe’s escalating war: in part out of moral principle, in part as a matter of practical necessity, and in part for political reasons. Few Americans wished to participate in the devastating battles that ravaged Europe, and Wilson did not want to risk losing his reelection by ordering an unpopular military intervention. Wilson’s “neutrality” did not mean isolation from all warring factions, but rather open markets for the United States and continued commercial ties with all belligerents. For Wilson, the conflict did not reach the threshold of a moral imperative for U.S. involvement; it was largely a European affair involving numerous countries with whom the United States wished to maintain working relations. In his message to Congress in 1914, the president noted that “Every man who really loves America will act and speak in the true spirit of neutrality, which is the spirit of impartiality and fairness and friendliness to all concerned.”
Wilson understood that he was already looking at a difficult reelection bid. He had only won the 1912 election with 42 percent of the popular vote, and likely would not have been elected at all had Roosevelt not come back as a third-party candidate to run against his former protégée Taft. Wilson felt pressure from all different political constituents to take a position on the war, yet he knew that elections were seldom won with a campaign promise of “If elected, I will send your sons to war!” Facing pressure from some businessmen and other government officials who felt that the protection of America’s best interests required a stronger position in defense of the Allied forces, Wilson agreed to a “preparedness campaign” in the year prior to the election. This campaign included the passage of the National Defense Act of 1916, which more than doubled the size of the army to nearly 225,000, and the Naval Appropriations Act of 1916, which called for the expansion of the U.S. fleet, including battleships, destroyers, submarines, and other ships.
As the 1916 election approached, the Republican Party hoped to capitalize on the fact that Wilson was making promises that he would not be able to keep. They nominated Charles Evans Hughes, a former governor of New York and sitting U.S. Supreme Court justice at the time of his nomination. Hughes focused his campaign on what he considered Wilson’s foreign policy failures, but even as he did so, he himself tried to walk a fine line between neutrality and belligerence, depending on his audience. In contrast, Wilson and the Democrats capitalized on neutrality and campaigned under the slogan “Wilson—he kept us out of war.” The election itself remained too close to call on election night. Only when a tight race in California was decided two days later could Wilson claim victory in his reelection bid, again with less than 50 percent of the popular vote. Despite his victory based upon a policy of neutrality, Wilson would find true neutrality a difficult challenge. Several different factors pushed Wilson, however reluctantly, toward the inevitability of American involvement.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'U.s. history' conversation and receive update notifications?