| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
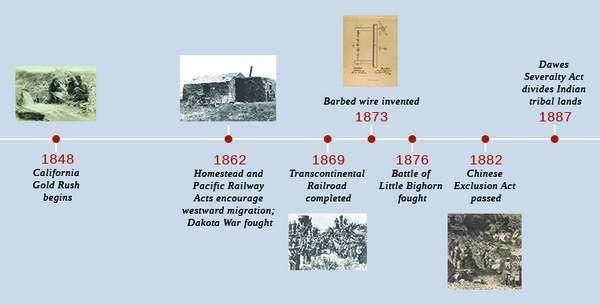
While a small number of settlers had pushed westward before the mid-nineteenth century, the land west of the Mississippi was largely unexplored. Most Americans, if they thought of it at all, viewed this territory as an arid wasteland suitable only for Indians whom the federal government had displaced from eastern lands in previous generations. The reflections of early explorers who conducted scientific treks throughout the West tended to confirm this belief. Major Stephen Harriman Long, who commanded an expedition through Missouri and into the Yellowstone region in 1819–1820, frequently described the Great Plains as a arid and useless region, suitable as nothing more than a “great American desert.” But, beginning in the 1840s, a combination of economic opportunity and ideological encouragement changed the way Americans thought of the West. The federal government offered a number of incentives, making it viable for Americans to take on the challenge of seizing these rough lands from others and subsequently taming them. Still, most Americans who went west needed some financial security at the outset of their journey; even with government aid, the truly poor could not make the trip. The cost of moving an entire family westward, combined with the risks as well as the questionable chances of success, made the move prohibitive for most. While the economic Panic of 1837 led many to question the promise of urban America, and thus turn their focus to the promise of commercial farming in the West, the Panic also resulted in many lacking the financial resources to make such a commitment. For most, the dream to “Go west, young man” remained unfulfilled.
While much of the basis for westward expansion was economic, there was also a more philosophical reason, which was bound up in the American belief that the country—and the “heathens” who populated it—was destined to come under the civilizing rule of Euro-American settlers and their superior technology, most notably railroads and the telegraph. While the extent to which that belief was a heartfelt motivation held by most Americans, or simply a rationalization of the conquests that followed, remains debatable, the clashes—both physical and cultural—that followed this western migration left scars on the country that are still felt today.
The concept of Manifest Destiny found its roots in the long-standing traditions of territorial expansion upon which the nation itself was founded. This phrase, which implies divine encouragement for territorial expansion, was coined by magazine editor John O’Sullivan in 1845, when he wrote in the United States Magazine and Democratic Review that “it was our manifest destiny to overspread the continent allotted by Providence for the free development of our multiplying millions.” Although the context of O’Sullivan’s original article was to encourage expansion into the newly acquired Texas territory, the spirit it invoked would subsequently be used to encourage westward settlement throughout the rest of the nineteenth century. Land developers, railroad magnates, and other investors capitalized on the notion to encourage westward settlement for their own financial benefit. Soon thereafter, the federal government encouraged this inclination as a means to further develop the West during the Civil War, especially at its outset, when concerns over the possible expansion of slavery deeper into western territories was a legitimate fear.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'U.s. history' conversation and receive update notifications?