| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Activity:
Recognise the place value of digits in whole numbers [LO 1.4]
Recognise and represent whole numbers in order to describe and compare them [LU 1.3]
OUR MODERN NUMBER SYSTEM: THE DECIMAL SYSTEM

1. Now let’s look at a bigger number. Just what does the number 1 111 mean, and why? Try to write down what it means:
One might say this is what it means:
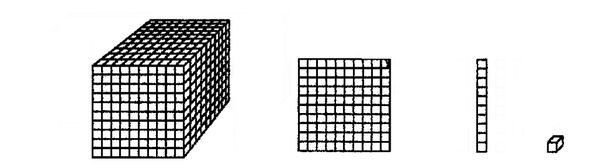
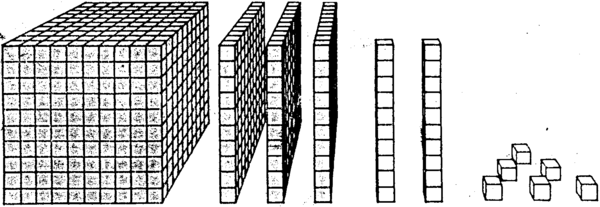
2. What number do you think this diagram represents?

| THOUSANDS | HUNDREDS | TENS | UNITS |
| 1 000 | 100 | 10 | 1 |
| 10 x 10 x 10 | 10 x 10 | 10 | 1 |
Recap: Our Decimal Number System
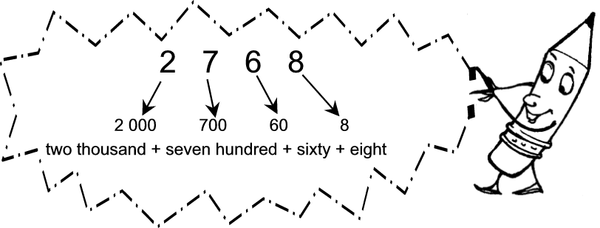
In our number system we have nine symbols and “0”. We use these symbols, 1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6; 7; 8; 9 and 0 to make any and all the numbers we need. We use the position of the digit in the number to indicate its value. So in the number 2 768 the 7 means 700 because of where it is in the number.
If there are no thousands (or digits in the other columns) we use 0 as a place holder.
Note: the 0 cannot be left out. If we left out the 0 the value of the whole number would change (e.g. 10 291 would become 1 291) so the 0 is very important.
Now complete the ones below:
| 2 768 = 2 000 700 60 8 |
| 7 834 = |
| 2 056 = |
| 8 503 = |
| 1 940 = |
| 16 473 = |
| 25 809 = |
Note also:
When we write big numbers we leave a space between the thousands and the hundreds. This makes it easier to read the number. Key 10 403 into your calculator. Unfortunately the calculator does not leave this space. Do you see it is not so easy to read this number on the calculator when there is no space between the thousands and the hundreds? Remember to leave the space in the correct place when you are writing big numbers.
MAKING NUMBERS AND ARRANGING THEM IN ORDER
3 967 = 3 000 900 60 7.
It can be written in columns like this:
| THOUSANDS1 000 | HUNDREDS100 | TENS10 | UNITS1 |
| 3 | 9 | 6 | 7 |
Because there are:
3 × 1 000 9 × 100 6 × 10 7
4. Now create the largest and the smallest numbers with the digits: 2; 8; 4; 1. Write them and two other numbers, still using only the digits 2; 8; 4; 1 in columns:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 4' conversation and receive update notifications?