| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
What is gambling all about?
ACTIVITY 1
To understand the context and vocabulary of probability
[LO 11.2, 5.1, 5.6]
1 The following very ordinary statements all deal with probability – but they are not all perfectly accurate. With your partner, study them and decide what is left unsaid, or what information you need to be able to evaluate them. Write down the results of your discussion.
For example : “The sun will come up tomorrow morning” really means: “If I go by the fact that the sun has come up every morning of my life, I am very certain that it will happen again tomorrow morning.”
1.1 If I toss a coin, there is a 50:50 chance that it will land tails up.
1.2 Kevin is certain to phone me tonight.
1.3 It is virtually impossible to win the lottery.
1.4 If you have a positive HIV test, then you will die of AIDS.
1.5 You are more likely to die of a spider-bite than of a lightning strike.
1.6 If you are told that every raffle ticket has two numbers, you have a double chance to win.
1.7 If you don’t play the Lotto, you are certain not to win.
1.8 In a room of 24 people, you are likely to find two people with the same birthday.
1.9 There is a 25% chance of rain tomorrow.
1.10 You are as likely to get a three as a four when you throw a die.
2 Refer to the following scale
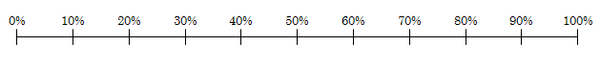
2.1 I will throw a six with an ordinary die.
2.2 If you pick a Smartie with your eyes closed, it will be a red one.
2.3 I will visit a friend next weekend.
2.4 The numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 are equally likely from throwing a die.
2.5 I will meet the president of South Africa someday.
2.6 I will stay the same height for the next year.
2.7 I will get a cold next winter.
2.8 I will be the president of South Africa someday.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 9' conversation and receive update notifications?