| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In the vapor phase, hydrogen fluoride is monomeric above 80 °C, but at lower temperatures it associates into oligomers and small polymers, e.g., cyclic (HF) 6 , as a consequence of strong intermolecular hydrogen bonds. As a pure liquid (Mp = -83 °C, Bp = 19.5 °C) hydrogen fluoride is extensively associated by strong hydrogen bonding to form zig-zag polymers ( [link] ).
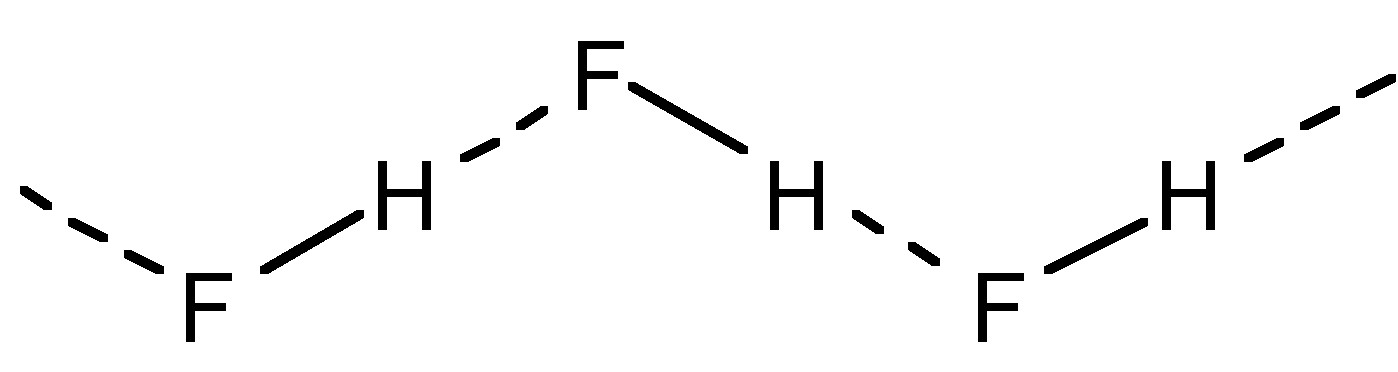
Hydrogen fluoride has a high dielectric constant (84.2) and as such is a good solvent for polar molecules. However, it is not a good solvent for salts (even fluorides) because it does not solvate cations too well. Despite this, it is useful as a solvent because it is non-oxidizing and easy to evaporate off products.
In a similar manner to water, hydrogen fluoride self-ionizes, [link] . Salts of H 2 F + are known and the F- anion is further solvated by the HF to form a series of salts, [link] . The complex anion HF 2 - is also formed in aqueous solutions of hydrogen fluoride (pK = 0.7).
Hydrogen fluoride is actually a weak acid in aqueous solution with a low pK = 3.5. In fact, HF is a weaker acid that the other halogen analogs:
This trend is despite the fluorine being more electronegative than the other halogens, but is consistent with the strength of the H-F bond (568 kJ/mol).
Hydrogen fluoride is used as a non-oxidizing acid for the hydrolysis of proteins and acid catalyzed condensation reaction. The stability of its salt (HF 2 - ) allow for the study of very strong acids, [link] and [link] .
The acidity of HF may be increased sufficiently by the addition of a fluoride acceptor (e.g., SbF 5 ) to facilitate the reaction with a weak base such as benzene, [link] .
Finally, hydrogen fluoride can be used in the synthesis of other fluorine-containing compounds:

Organic compounds in which some or all of the hydrogen atoms are replaced by fluorine have unique (and often important) properties. The high stability of fluorocarbon compounds is a consequence of the C-F bond energy (486 kJ/mol) in comparison with that of C-H (415 kJ/mol); however, while kinetically stable, fluorocarbons are not necessarily particularly thermodynamically stable.
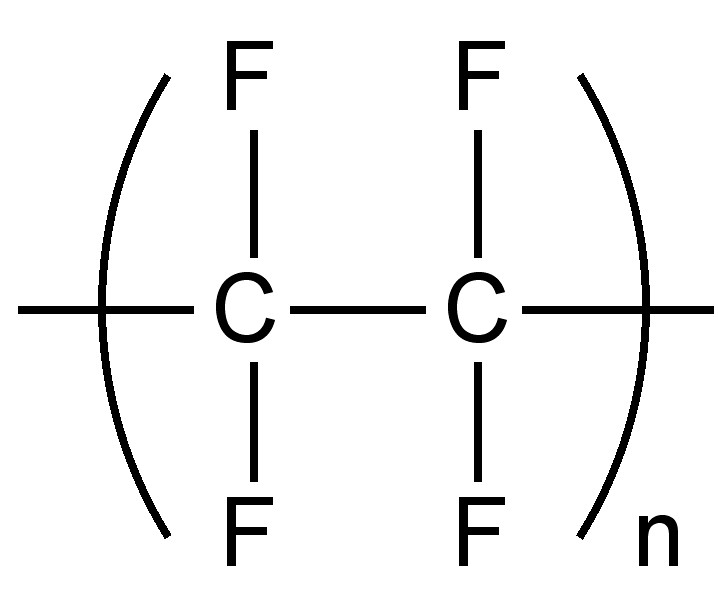
Replacement of hydrogen with fluorine results in an increased density; since the small size of fluorine means that the minimal distortion or structural change occurs as a result of the substitution. As with metal salts, the weak inter-molecular forces means that completely fluorinated organic compounds have low boiling points. One attribute of the low inter-molecular forces is the low coefficient of friction for fluoropolymers such as polytetrafluoroethylene, commonly known as Teflon ( [link] ).
The simplest route to a fluorocarbon compounds involves the direct replacement of another halogen by a metal fluoride, [link] . The driving force for this reaction depends on the free-energy difference of MF and MCl, which is related to the difference in lattice energies. Thus, the larger the metal cation, the more favored the reaction. In this regard, AgF and CsF are the most effective fluorination agent.
Anhydrous hydrogen fluoride (HF) reacts with chlorocarbon compounds in the presence of a catalyst such as SbCl 5 or CrF 4 , [link] . However, elevated temperatures (50 – 150 °C) and high pressures (50 – 500 psi) are required.
The direct replacement of hydrogen with fluorine is possible if the reaction is carried out under dilute conditions in the presence of a catalyst, [link] .
Sulfur tetrafluoride (SF 4 ) is a particularly selective fluorination agent. It can be used to convert ketones to difluoro compounds, [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry of the main group elements' conversation and receive update notifications?