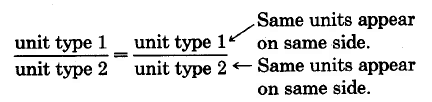. Find the cross product.
This means that
, or, 5 is to 4 as 20 is to 6.
Find the cross product.
The means that
, or, 16 is to 3 as 64 is to 12.
Find the cross products.
Practice set b
Find the unknown number in each proportion.
Proportions involving rates
Recall that a rate is a comparison, by division, of unlike denominate numbers. We must be careful when setting up proportions that involve rates. The
form is important. For example, if a rate involves two types of units, say unit type 1 and unit type 2, we can write
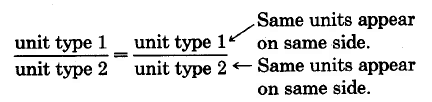
or
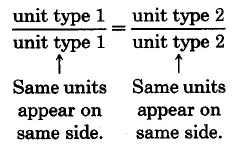
Both cross products produce a statement of the type
which we take to mean the comparison
Examples of correctly expressed proportions are the following:
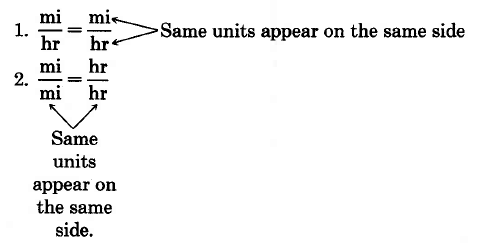
However, if we write the same type of units on different sides, such as,
the cross product produces a statement of the form

We can see that this is an incorrect comparison by observing the following example: It is
incorrect to write
for two reason.
- The cross product is numerically wrong:
.
- The cross product produces the statement “hooks are to hooks as poles are to poles,” which makes no sense.
Exercises
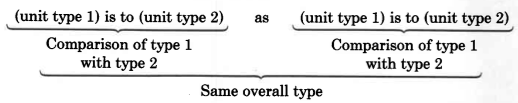
A statement that two ratios or
are equal is called a
.
For the following 9 problems, write each proportion in fractional form.
3 is to 7 as 18 is to 42.
1 is to 11 as 3 is to 33.
9 is to 14 as 27 is to 42.
6 is to 90 as 3 is to 45.
5 liters is to 1 bottle as 20 liters is to 4 bottles.
18 grams of cobalt is to 10 grams of silver as 36 grams of cobalt is to 20 grams of silver.
4 cups of water is to 1 cup of sugar as 32 cups of water is to 8 cups of sugar.
3 people absent is to 31 people present as 15 people absent is to 155 people present.
6 dollars is to 1 hour as 90 dollars is to 15 hours.
For the following 10 problems, write each proportion as a sentence.
3 joggers are to 100 feet as 6 joggers are to 200 feet
40 miles are to 80 miles as 2 gallons are to 4 gallons
1 person is to 1 job as 8 people are to 8 jobs
2,000 pounds are to 1 ton as 60,000 pounds are to 30 tons
For the following 10 problems, solve each proportion.
For the following 5 problems, express each sentence as a proportion then solve the proportion.
5 hats are to 4 coats as
hats are to 24 coats.
cushions are to 2 sofas as 24 cushions are to 16 sofas.
1 spacecraft is to 7 astronauts as 5 spacecraft are to
astronauts.
56 microchips are to x circuit boards as 168 microchips are to 3 circuit boards.
18 calculators are to 90 calculators as
students are to 150 students.
dollars are to $40,000 as 2 sacks are to 1 sack.
Indicate whether the proportion is true or false.
Exercises for review
(
[link] ) Use the number 5 and 7 to illustrate the commutative property of addition.
(
[link] ) Use the numbers 5 and 7 to illustrate the commutative property of multiplication.
(
[link] ) Find the difference.
.
(
[link] ) Find the product.
.
(
[link] ) Write the simplified fractional form of the rate “sixteen sentences to two paragraphs.”