| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Sản phẩm có thể lạnh đông trong thời gian thích hợp, tốc độ dòng thổi của không khí nên đạt ở mức cân bằng cao. Để đạt được tốc độ lạnh đồng nhất sau khi qua thiết bị lạnh đông, dòng không khí thổi vào yêu cầu phải giống nhau trên mỗi con cá và mỗi bao gói.
Tốc độ không khí thổi 5 m/s thường được áp dụng cho hầu hết các dạng lạnh đông bằng khí thổi.
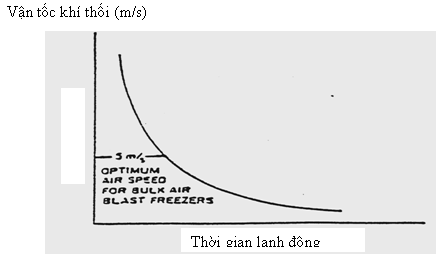
Hình 4.2. Mối quan hệ giữa thời gian lạnh đông với tốc độ không khí trong thiết bị lạnh đông bằng khí thổi
Thiết bị lạnh đông khí thổi liên tục có thể điều chỉnh tốc độ khí thổi vào khi vượt quá giá trị cho phép. Tốc độ dòng khí thổi cao, khoảng 10 - 15 m/s có thể mang lại giá trị kinh tế cao cho thiết bị lạnh đông dạng liên tục.
Nhược điểm của thiết bị lạnh đông dạng khí thổi là tính không hiệu quả và dòng khí thổi vào không đồng nhất trên sản phẩm.

Hình 4.3. Tủ đông gió
Hình 4.3 mô tả dạng thiết bị lạnh đông dạng khí thổi. Không khí lạnh chuyển động từ phía sau tới và trở lại dàn lạnh ở khoảng trống phía dưới. Tủ gồm nhiều mô đun độc lập với nhau, nhờ đó có thể điều chỉnh năng suất lạnh của nó dễ dàng.
Lạnh đông dạng đĩa được ứng dụng cho lạnh đông cá khối (block) nhưng nó không linh hoạt như dạng khí thổi. Thiết bị có thể là dạng đứng hoặc nằm ngang tùy theo cách sắp xếp của đĩa. Các đĩa được làm bằng nhôm, dạng cắt ngang, sắp xếp thành hàng và chất lỏng làm lạnh sẽ đi qua đó. Quá trình trao đổi nhiệt diễn ra ngang qua mặt trên và mặt dưới của đĩa. Quá trình lạnh đông được hình thành nhờ sự tiếp xúc trực tiếp giữa đĩa lạnh và sản phẩm.
Kích cỡ tối đa của khối sản phẩm ứng dụng trong phương pháp này thường là 1,07 mm x 535 mm. Tuy nhiên, kích cỡ của khối sản phẩm có thể thay đổi tùy theo sản phẩm và bề dày của khối sản phẩm có thể thay đổi dao động trong khoảng từ 25 đến 130 mm. Kích cỡ của khối sản phẩm được chọn lựa phụ thuộc vào loại cá đem đi lạnh đông.
* Ảnh hưởng của mức độ tiếp xúc các bề mặt truyền nhiệt trong tủ đông tiếp xúc
Mức độ tiếp xúc và khả năng truyền nhiệt từ thực phẩm vào dàn lạnh giảm do:
Hình 4.4. Tủ đông tiếp xúc và các yếu tố ảnh hưởng đến mức độ tiếp xúc, truyền nhiệt trong tủ đông tiếp xúc
Biện pháp khắc phục:
Để tăng khả năng truyền nhiệt của thực phẩm trong tủ đông tiếp xúc có thể áp dụng các biện pháp:
- Thay khay đựng khuôn bằng khung ghép khuôn
- Dùng thép không rỉ làm khuôn
- Sử dụng các khuôn có kích thước phù hợp với sản phẩm trong khuôn, không để dư thể tích khuôn khi sản phẩm đã đóng băng
- Dùng nắp đậy khuôn phù hợp
- Đảm bảo lực ép nén đều và đủ cho dàn lạnh
Đây là loại thiết bị thường được ứng dụng để cấp đông sản phẩm IQF. Dạng thiết bị lạnh đông này ít được sử dụng rộng rãi trong công nghệ chế biến cá lạnh đông mà chỉ thường được sử dụng để lạnh đông các sản phẩm đặc biệt hoặc sản phẩm có giá trị kinh tế cao.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chế biến thủy sản' conversation and receive update notifications?