| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The above experiment on flame tests relates to the line emission spectra of the metals. These line emission spectra are a direct result of the arrangement of the electrons in metals.
| Element | No. of energy levels | No. of core electrons | No. of valence electrons | Electron configuration (standard notation) |
Earlier in this chapter, we talked about different 'models' of the atom. In science, one of the uses of models is that they can help us to understand the structure of something that we can't see. In the case of the atom, models help us to build a picture in our heads of what the atom looks like.
Models are often simplified. The small toy cars that you may have played with as a child are models. They give you a good idea of what a real car looks like, but they are much smaller and much simpler. A model cannot always be absolutely accurate and it is important that we realise this so that we don't build up a false idea about something.
In groups of 4-5, you are going to build a model of an atom. Before you start, think about these questions:
As a group, share your ideas and then plan how you will build your model. Once you have built your model, discuss the following questions:
Now look at what other groups have done. Discuss the same questions for each of the models you see and record your answers.
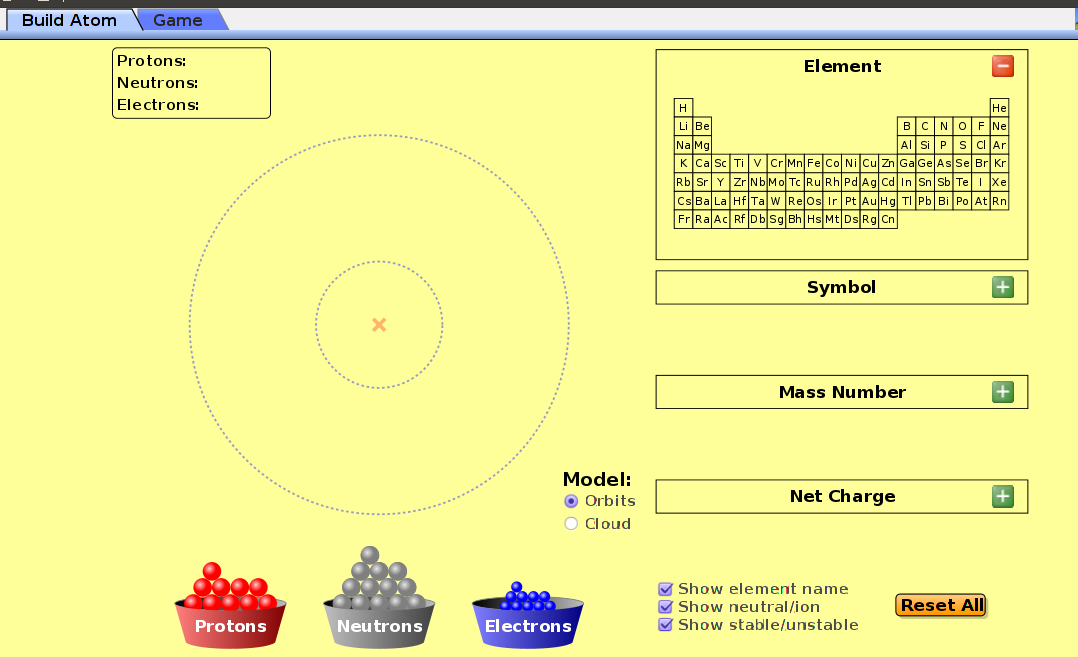
The following simulation allows you to build an atom
run demo

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry grade 10 [caps]' conversation and receive update notifications?