| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
It is not possible to measure lattice energies directly. However, the lattice energy can be calculated using the equation given in the previous section or by using a thermochemical cycle. The Born-Haber cycle is an application of Hess’s law that breaks down the formation of an ionic solid into a series of individual steps:
[link] diagrams the Born-Haber cycle for the formation of solid cesium fluoride.
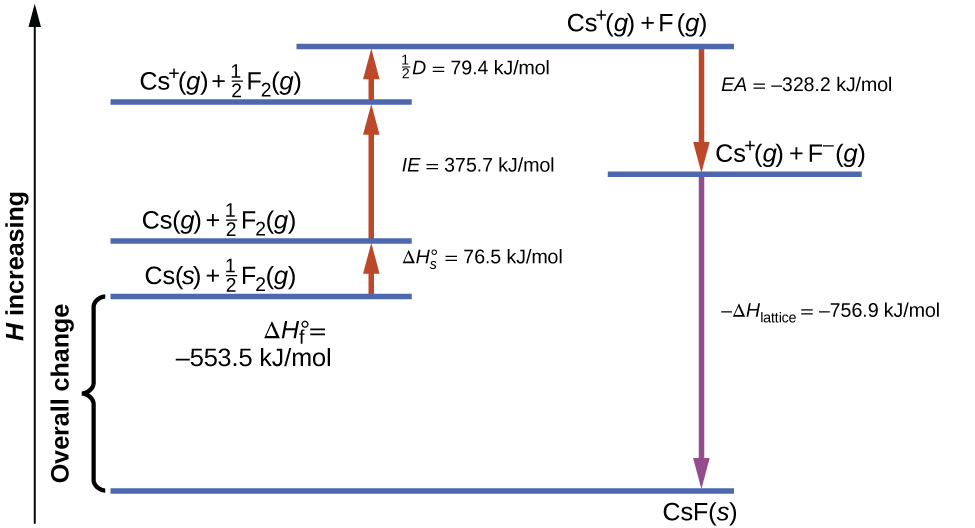
We begin with the elements in their most common states, Cs( s ) and F 2 ( g ). The represents the conversion of solid cesium into a gas, and then the ionization energy converts the gaseous cesium atoms into cations. In the next step, we account for the energy required to break the F–F bond to produce fluorine atoms. Converting one mole of fluorine atoms into fluoride ions is an exothermic process, so this step gives off energy (the electron affinity) and is shown as decreasing along the y -axis. We now have one mole of Cs cations and one mole of F anions. These ions combine to produce solid cesium fluoride. The enthalpy change in this step is the negative of the lattice energy, so it is also an exothermic quantity. The total energy involved in this conversion is equal to the experimentally determined enthalpy of formation, of the compound from its elements. In this case, the overall change is exothermic.
Hess’s law can also be used to show the relationship between the enthalpies of the individual steps and the enthalpy of formation. [link] shows this for cesium chloride, CsCl 2 .
| Enthalpy of sublimation of Cs( s ) | |
| One-half of the bond energy of Cl 2 | |
| Ionization energy of Na( g ) | |
| Negative of the electron affinity of Cl | |
| Negative of the lattice energy of NaCl( s ) | |
| Enthalpy of formation of NaCl( s ), add steps 1–5 |
Thus, the lattice energy can be calculated from other values. For cesium chloride, using this data, the lattice energy is:
The Born-Haber cycle may also be used to calculate any one of the other quantities in the equation for lattice energy, provided that the remainder is known. For example, if the relevant enthalpy of sublimation ionization energy (IE), bond dissociation enthalpy (D), lattice energy Δ H lattice, and standard enthalpy of formation are known, the Born-Haber cycle can be used to determine the electron affinity of an atom.
Lattice energies calculated for ionic compounds are typically much higher than bond dissociation energies measured for covalent bonds. Whereas lattice energies typically fall in the range of 600–4000 kJ/mol (some even higher), covalent bond dissociation energies are typically between 150–400 kJ/mol for single bonds. Keep in mind, however, that these are not directly comparable values. For ionic compounds, lattice energies are associated with many interactions, as cations and anions pack together in an extended lattice. For covalent bonds, the bond dissociation energy is associated with the interaction of just two atoms.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?