| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Let’s now apply what we have learned about gravity and spacetime curvature to the issue we started with: the collapsing core in a very massive star. We saw that if the core’s mass is greater than about 3 M Sun , theory says that nothing can stop the core from collapsing forever. We will examine this situation from two perspectives: first from a pre-Einstein point of view, and then with the aid of general relativity.
Let’s begin with a thought experiment. We want to know what speeds are required to escape from the gravitational pull of different objects. A rocket must be launched from the surface of Earth at a very high speed if it is to escape the pull of Earth’s gravity. In fact, any object—rocket, ball, astronomy book—that is thrown into the air with a velocity less than 11 kilometers per second will soon fall back to Earth’s surface. Only those objects launched with a speed greater than this escape velocity can get away from Earth.
The escape velocity from the surface of the Sun is higher yet—618 kilometers per second. Now imagine that we begin to compress the Sun, forcing it to shrink in diameter. Recall that the pull of gravity depends on both the mass that is pulling you and your distance from the center of gravity of that mass. If the Sun is compressed, its mass will remain the same, but the distance between a point on the Sun’s surface and the center will get smaller and smaller. Thus, as we compress the star, the pull of gravity for an object on the shrinking surface will get stronger and stronger ( [link] ).
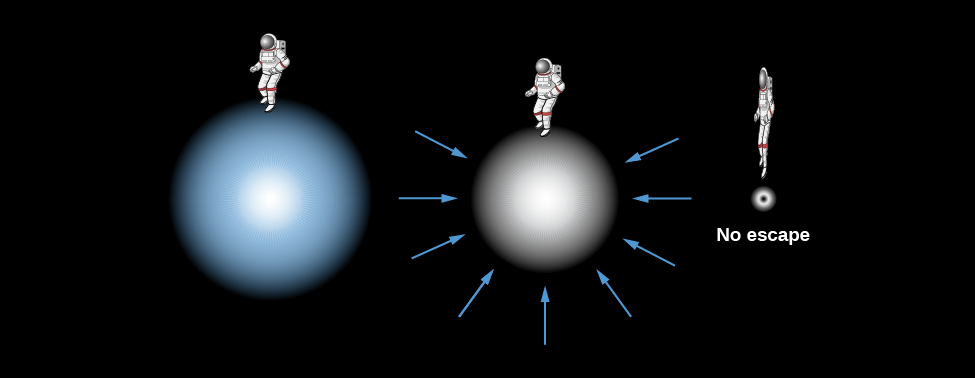
When the shrinking Sun reaches the diameter of a neutron star (about 20 kilometers), the velocity required to escape its gravitational pull will be about half the speed of light. Suppose we continue to compress the Sun to a smaller and smaller diameter. (We saw this can’t happen to a star like our Sun in the real world because of electron degeneracy, i.e., the mutual repulsion between tightly packed electrons; this is just a quick “thought experiment” to get our bearings).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?