| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
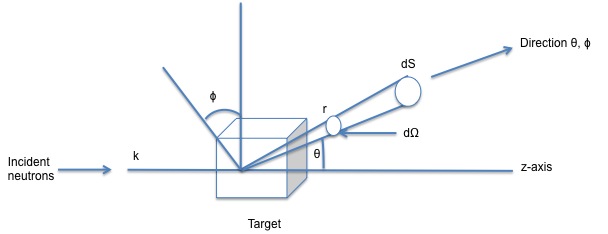
The incident beam encounters the target and the scattered wave produced from the collision is detected by a detector at a defined position given by the angles θ, ϕ which are joined by the dΩ. In this scenario there is assumed that there is no transferred energy between the nucleus of the atoms and the neutron ejected, leads to an elastic scattering.
When there is an interest in calculating the diffracted intensities the cross sectional area needs to be separated into scattering and absorption respectively. In relation to the energies of these there is moderately large range for constant scattering cross section. Also, there is a wide range cross sections close to the nuclear resonance. When the energies applied are less than the resonance the scattering length and scattering cross section are moved to the negative side depending on the structure being examined. This means that there is a shift on the scattering, therefore the scattering will not be in a 180° phase. When the energies are higher that resonance it means that the cross section will be asymptotic to the nucleus area. This will be expected for spherical structures. There is also resonance scattering when there are different isotopes because each produce different nuclear energy levels.
Usually in every material, atoms will be arranged differently. Therefore, neutrons when scattered will be either coherently or incoherently. It is convenient to determine the differential scattering cross section, which is given by [link] , where b represents the mean scattering length of the atoms, k is the scattering vector, r n is the position of the vector of the analyzed atom and lastly N is the total number of atoms in the structure.This equation can be separated in two parts, which one corresponds to the coherent scattering and the incoherent scattering as labeled below. Usually the particles scattered will be coherent which facilitates the solution of the cross section but when there is a difference in the mean scattering length, there will be a complete arrangement of the formula and these new changes (incoherent scattering) should be considered. Incoherent scattering is usually due to the isotopes and nuclear spins of the atoms in the structure.
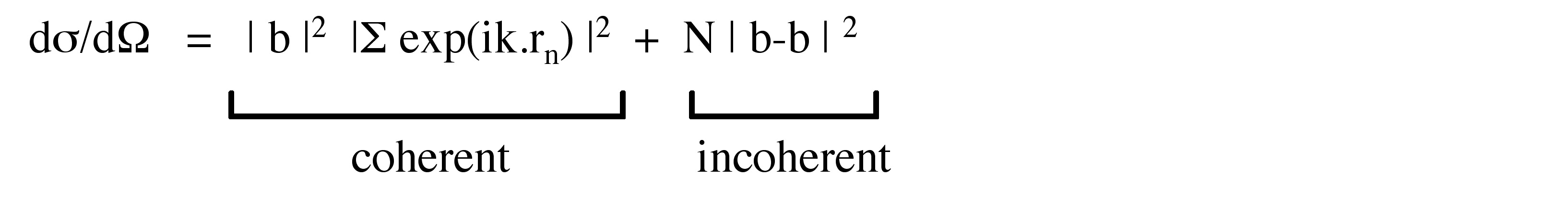
The ability to distinguish atoms with similar atomic number or isotopes is proportional to the square of their corresponding scattering lengths. There are already known several coherent scattering lengths of some atoms which are very similar to each other. Therefore, it makes even easier to identify by neutrons the structure of a sample. Also neutrons can find ions of light elements because they can locate very low atomic number elements such as hydrogen. Due to the negative scattering that hydrogen develops it increases the contrast leading to a better identification of it, although it has a very large incoherent scattering which causes electrons to be removed from the incident beam applied.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?