| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
CLASS WORK
1.1 Yes, any informal “proof” is acceptable.
1.2 As 1.1
1.3 Zero and negative numbers make an appearance. The explanation is not important – only the thinking that the learner does.
2.1 N 0 = {0 ; 1 ; 2 ; . . . } and Z = { . . . –3 ; –2 ; –1 ; 0 ; 1 ; 2 ; 3 ; . . .}
3. Here are the fractions. Explain carefully that integers can also be written as fractions – in fact it is quite often a useful technique.
4.1 Not everyone will be able to cope with this. R ` gives the answers that are obtained when square roots of negative numbers (inter alia) is taken.
TASK
2. Point out to learners that zero is missing from the table.
HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT
1. Zero is needed because:
The principle behind place values is totally dependent on having a symbol for zero.
It separates positive and negative numbers.
It symbolises “nothing”.
Algebraically it is defined as: a + (– a )
2. Complex numbers – don’t expect too much.
If one uses the symbol i for , then we can represent non–real numbers as follows: = = = =
3 + 5i and 2,5 – 16i are examples of non–real numbers, and each consists of two parts: a real part and a non-real part. The most important consequences of this are that one must be careful when doing arithmetic calculations, and that these numbers cannot be arranged in ascending order!
3. Any reasonable answer can be accepted. This might be a good opportunity to have learners evaluating each other’s number systems.
ENRICHMENT ASSIGNMENT
If there is time, one can go through this work, particularly with a strong group.
4.1 Non-repeating; although 3,030030003000030… has a pattern, it does not repeat.
4.2 Emphasise that the first one is NOT equal to π. The two others must be simplified properly.
4.3.1
4.3.2
4.3.3
4.3.4
CLASS ASSIGNMENT
The aim of this exercise is to familiarise learners with unsimplified values, so that they can learn to estimate. It is very important that they mentally simplify correctly so that they can start guessing the magnitudes. Then the values have to be arranged in at least the correct order. If the spaces in between are in reasonable proportion, that is a bonus. This shows the order:
1.1 0,00 ; 1 ; 2 ; 3,0 ; 4 ; 5,0000 ; 5+2 ; 6 ; 9–1
1.2 –4 ; –3 ; –1 ; 3–3 ; 2 ; 5
1.3 ; ; 0.666 ; ; ; 1,000 ; 0,2+1 ; 1.75
1.4 ; ; –5,5 ; ; –2,5 ; 5,55 ;
1.5 ; ; ; ; ; ; ; –1
1.6 ; ; ; ; ; +1 ; ;
ENRICHMENT ASSIGNMENT
1.1 5,6<5,7; 3+9 = 4×3; –1>–2; 3>–3; <
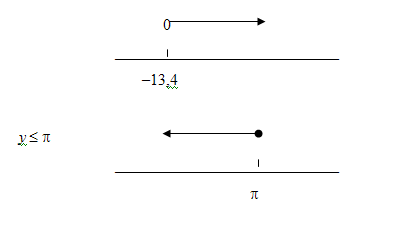
2.1 y >–13,4
GROUP ASSIGNMENT
These are the simplified values in the original order:
1.1 –8 ; 12 ; –6 ; 2 ; 10 ; 3 ; 5 ; 3,44… ; 3
1.2 2 ; 0,3… ; 1,3… ; 0,5 ; 0,5 ; 0,05 ; 0,005
1.3 3 ; 3,5 ; 3,14 ; 3,142857… ; 3,1415929… ; 3,1415926… (the last one is π)
These are the same values in the correct order:
1.1 –8 ; –6 ; 2 ; 3 ; 3,44… ; 5 ; 10 ; 12
1.2 0,005 ; 0,05 ; 0,3… ; 0,5 ; 1,3… ; 2
1.3 3 ; 3,14 ; π ; 3,1415929… ; 3,142857…
CLASS WORK
This exercise has been designed to give learners a feeling for the consequences of rounding (approximated answers). They often put complete unthinking faith in their calculators’ answers.
1.1 Note the notation as well as the number of decimal places.
1.2 Again, notation as well as number of decimal places.
1.3 Emphasise once again that an approximation to π is not equal to π.
Discuss the meaning of the term “approximately equal to”.
3. Answers: 1,03 ; 2,83 ; 15,71 ; 12 ; 1,0 (the zero must be there).
CLASS WORK
Learners often have difficulties with conversions – you might have to supply lots of help and guidance.
1.3 The months don’t have the same number of days; simply multiplying will not give the best answer. Find out which months are meant and don’t forget leap years!
1.4 Why division? Help them develop strategies.
3. Similar problems to 1.3. The answer can be approximated. Explain why this acceptable. This problem will motivate them to appreciate the advantages of scientific notation: ≈ 3 157 056 000 seconds.
5.1 9,1 × 10 28
5.2 24 km
5.3 100 litres

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 9' conversation and receive update notifications?