| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Graphing, like algebraic generalizations, is a difficult topic because many students know how to do it but are not sure what it means .
For instance, consider the following graph:
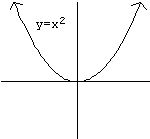
If I asked you “Draw the graph of ” you would probably remember how to plot points and draw the shape.
But suppose I asked you this instead: “Here’s a function, . And here’s a shape, that sort of looks like a U. What do they actually have to do with each other?” This is a harder question! What does it mean to graph a function?
The answer is simple, but it has important implications for a proper understanding of functions. Recall that every point on the plane is designated by a unique pair of coordinates: for instance, one point is . We say that its -value is 5 and its -value is 3.
A few of these points have the particular property that their -values are the square of their -values. For instance, the points , , and all have that property. and do not.
The graph shown—the pseudo-U shape—is all the points in the plane that have this property . Any point whose -value is the square of its -value is on this shape; any point whose -value is not the square of its -value is not on this shape. Hence, glancing at this shape gives us a complete visual picture of the function if we know how to interpret it correctly .
Remember that every function specifies a relationship between two variables. When we graph a function, we put the independent variable on the -axis, and the dependent variable on the -axis.
For instance, recall the function that describes Alice’s money as a function of her hours worked. Since Alice makes $12/hour, her financial function is . We can graph it like this.
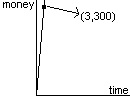
This simple graph has a great deal to tell us about Alice’s job, if we read it correctly.
Consider now the following, more complicated graph, which represents Alice’s hair length as a function of time (where time is now measured in weeks instead of hours).
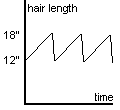
What does this graph tell us? We can start with the same sort of simple analysis.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Math 1508 (lecture) readings in precalculus' conversation and receive update notifications?