| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
H.2_2a: bộ phận khuếch đại thì phi tuyến. Motor được giả sử tuyến tính hay hoạt đôïng ở vùng tuyến tính. Những tính chất động của nó biểu diển bằng phương trình (2.20).
H.2_2b: cùng hệ thống trên nhưng bộ phận khuếch đại thì tuyến tính.
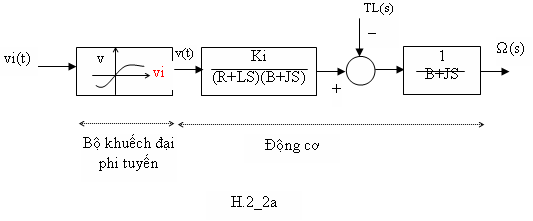
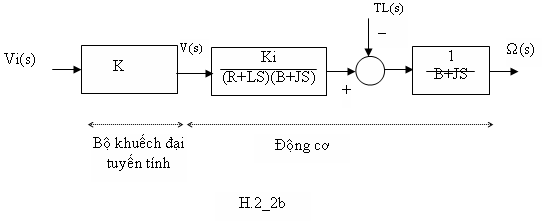
Lưu ý là H.2_2a, vì bộ khuếch đại là phi tuyến, nên không có hàm chuyển giữa ngõ vào và ngõ ra của nó. Giả sử chúng chỉ có thể xác định bằng hệ thức liên hệ giữa hai biến vi(t) và v(t) mà thôi. Ngược lại, H2_2b, hàm chuyển giữa ngõ vào và ngõ ra của bộ khuếch đại là K. Và ,
V(s)=K.Vi(s).
Một thành phần được dùng nhiềøu trong các sơ đồ khối của hệ điều khiển, đó là bộ cảm biến (sensing device), nó đóng vai trò so sánh tín hiệu và thực hiện vài thuật toán đơn giản như cộng, trừ, nhân và đôi khi tổ hợp của chúng.
Bộ cảm biến có thể là một biến trở, một nhiïêt trở hoặc một linh kiện chuyển năng khác (transducer), cũng có thể là một mạch khuếch đại vi sai, mạch nhân ...
Sơ đồ khối của cảm biến trình bày ở H.2_3a,b,c,d.
+ H.2_3a,b,c: mạch cộng trừ thì tuyến tính. Nên các biến ở ngõ vào và ra có thể là biến theo t hoặc s ( biến đỏi Laplace ).
e(t) = r(t) -c(t) (2.22)
hoặc E(s)=R(s)-C(s) (2.23)
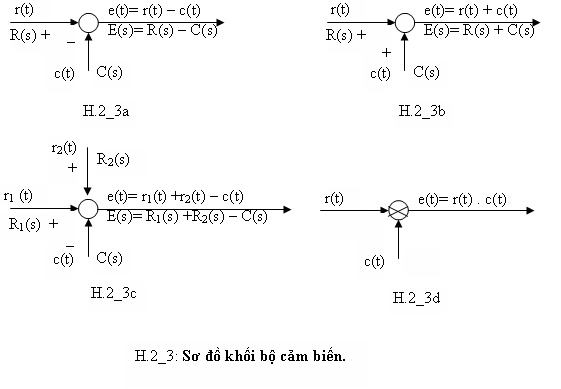
Ở H.2_3d, mạch nhân thì phi tuyến, nên liên hệ giữa input và output chỉ có thêû ở phạm vi thời gian (Time domain). Nghĩa là,
e(t)=r(t).c(t) (2.24)
Trong trường hợp này sẽ không đưa đến E(s)=R(s) .C(s).
Có thể dùng định lý chập phức (complexe_convolution) của biến đổi Laplace để đưa (2.24) đến :
E(s)=R(s)*C(s) (2.25)
Một hệ tự điều khiển tuyến tính có thể được trình bày bằng sơ đồ khối chính tắc như H.2_4. Trong đó :
r(t), R(s): tín hiệu tham khảo vào.
c(t), C(s): biến số được kiểm soát ở ngõ ra.
b(t), B(s): tín hiệu hồi tiếp.
e(t), E(s): tín hiệu sai biệt ( error ).
: Hàm chuyển vòng hở hoặc hàm chuyển đường trực tiếp
(forward path).
: Hàm chuyển vòng kín, hoặc tỉ số điều khiển .
H(s): Hàm chuyển hồi tiếp (feedback transfer )
G(s).H(s): Hàm chuyển đường vòng (loop transfer)
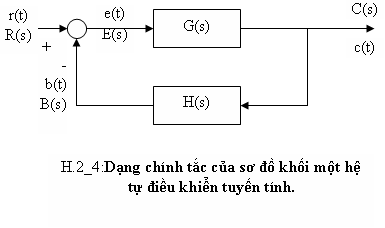
Từ H.2_4 ta có :
C(s)=G(s).E(s) (2.26)
E(s)=R(s) – B(s) (2.27)
B(s)=H(s).C(s) (2.28)
Thế (2.27) vào (2.26):
C(s)=G(s).R(s)-G(s).B(s) (2.29)
Thay (2.28) vào (2.29):
C(s)=G(s)R(s)-G(s).H(s)C(s) (2.30)
Từ phương trình cuối cùng suy ra hàm chuyển đôï lợi vòng kín:
(2.31)
H.2_5 trình bày sơ đồ khối nhiều biến, với p input và q output.
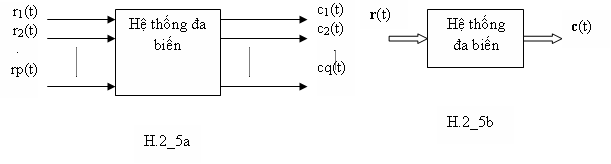
H.2_5b được dùng nhiều vì đơn giản. Sự nhiều input và output được biểu diễn bằng vector .
H.2_6 chỉ sơ đồ khối dạng chính tắc của hệ thống đa biến.

H.2_6: Sơ đồ khối dạng chính tắc của hệ đa biến.
Hàm chuyển được suy bằng cách dùng phép tính đại số các ma trận.
C(s) = G(s). E(s) (2.32)
E(s) = R(s) - B(s) (2.33)
B(s) = H(s). C(s) (2.34)
Ở đó : C(s) là ma trận qx1: vector output
E(s), B(s), R(s): đều là ma trận px1
G(s) và H(s) là ma trận qxp và pxq : ma trận chuyển.
Thay (2.34) vào (2.33) và rồi thay (2.33) vào (2.32) :
C(s)=G(s). R(s) – G(s). H(s).C(s) (2.35)
Giải C(s) từ (2.35) :
C(s)=[ I + G(s). H(s)]-1. G(s). R(s) (2.36)
Giả sử I + G(s). H(s) không kỳ dị (non singular).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Cơ sở tự động học' conversation and receive update notifications?