| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The turned-in knees of humans and of Australopithecus allow the feet to be aligned to the front.
This means that the ball of the foot and the big toe, in particular, plays an important role in walking.
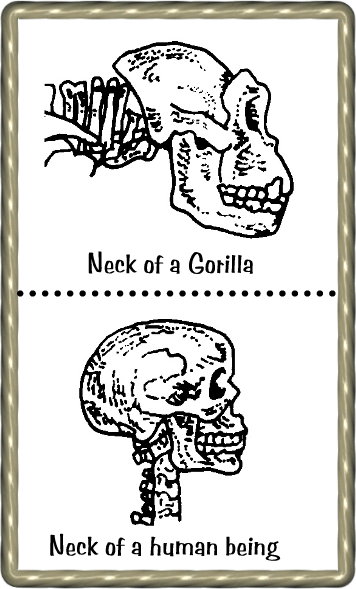
Source C
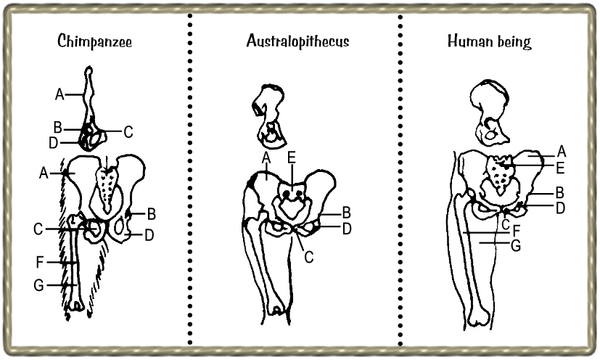 |
| Pelvic girdles and thighbones. The similarity of the human thighbone and that of Australopithecus is clearly identifiable. The vertical black line G indicates the axis along which the weight is transferred from the hip to the knee. A = os ileum (hipbone), B = socket for the thighbone, C = os pubis (pubic bone), D = os ischium, E = os sacrum, F = os femur (thighbone). |
Source D
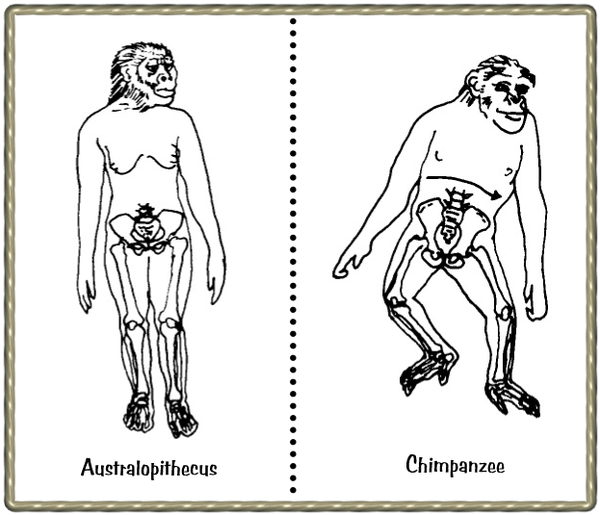 |
| With Australopithecus the knee joints were turned inwards, as with modern human beings and their footprints formed a similar pattern to ours. The chimpanzee has a waddling gait when it walks on hind legs only. |
Twelve years later, in 1936, Dr. Robert Boom discovered an adult skull at Sterkfontein (near Krugersdorp). He initially thought that he had found a female of a new species and named it Plesianthropus transvaalensis (Mrs. Ples). But further investigation revealed Mrs. Ples to be virtually identical to the Taung child.
a) Study the following and then answer the questions that are provided. First make a sketch illustrating similar circumstances at your home.

b) Develop a comic strip or an art song to give expression to the above information.
| Assessment standards(ASe) |
| LEARNING OUTCOME 1: HISTORICAL ENQUIRY- The learner will be able to use enquiry skills to investigate the past and present |
| 1.1 Access the sources |
| 1.2 Use the sources |
| 1.3 Communicate information from sources (reporting)) |
| LEARNING OUTCOME 2: HISTORICAL KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING – The learner will be able to demonstrate historical knowledge and understanding |
| 2.1 Understand chronology and time |
| 2.2 Supply reasons why an historical event took place (causes, effects) |
| 2.3 Differentiate between different periods (similarities, differences) |
| LEARNING OUTCOME 3: INTERPRETING HISTORY – The learner will be able to interpret aspects of history |
| 3.1 Be aware of more than one view of the past |
| 3.2 Distinguish between fact and opinion |
| 3.3 Reconstruct the past |
Activity 1
There are clear differences between apes and human beings. Man is the only primate to walk upright. The shape of the pelvis, the position of the femur, and the way in which the feet are put down, are very specific. A comparison between the build of the rest of the body and the brain indicates that the Australopithecus is related closer to man. There was a development pattern from Australopithecus through Homo habilis and Homo erectus to the modern day Homo sapiens .
Activity 2
Suppose this illustration is a representation of the Stone Age :
They lived in caves where they slept and kept food, and used tools, weapons and fire. Gathering food was the main activity. The men hunted and caught fish. The women and children gathered berries, wild fruit and root plants. They also hoarded food for the winter months and also prepared food. Tools were made of bone, stone and wood and gradually improved because they also manufactured arrows, axes and daggers. They could manufacture objects, e.g. “needles” that were used to sew clothing from wool and flax. Early man never stayed long in one place.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'History grade 7' conversation and receive update notifications?