| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
INTRODUCTION
The learning programme for grade six consists of five modules:
1. Number concept, Addition and Subtraction
2. Multiplication and Division
3. Fractions and Decimal fractions
4. Measurement and Time
5. Geometry; Data handling and Probability
COMMON AND DECIMAL FRACTIONS (LO 1; 2 AND 5)
LEARNING UNIT 1 FOCUSES ON COMMON FRACTIONS
1.1
1.2 = 1
1.3 = 1
1.4 =
1. Now that we have revised the addition of fractions, you shouldn’t have any difficulty with the following. Work on your own and calculate:
1.1 +
.................................................................................
.................................................................................
.................................................................................
.................................................................................
1.2 +
.................................................................................
.................................................................................
.................................................................................
.................................................................................
1.3 +
.................................................................................
.................................................................................
.................................................................................
.................................................................................
1.4 +
.................................................................................
.................................................................................
.................................................................................
.................................................................................
X 4X 4 We sometimes have to find a common denominator. In + forinstance, it is difficult to change thirds into quarters or quarters into thirds. You find the common denominator by multiplying the two denominators. In our example, the common denominator is 3 x 4 = 12. We refer to 12 as the smallest common multiple of 3 and 4.
X 3X 3 Thus: + ( = )
= + ( = )
=
This is what it looks like when we draw it:

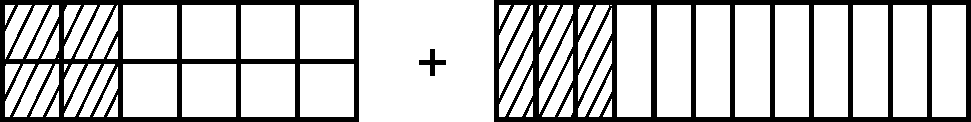
Learning Outcome 1: The learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent numbers and their relationships, and to count, estimate, calculate and check with competence and confidence in solving problems.
Assessment Standard 1.8: We know this when the learner estimates and calculates by selecting and using operations appropriate to solving problems that involve:
1.8.3 addition and subtraction of common fractions with denominators which are multiples of each other and whole numbers with common fractions (mixed numbers);

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 6' conversation and receive update notifications?