| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We have used factoring to solve quadratic equations, but it is a technique that we can use with many types of polynomial equations, which are equations that contain a string of terms including numerical coefficients and variables. When we are faced with an equation containing polynomials of degree higher than 2, we can often solve them by factoring.
A polynomial of degree n is an expression of the type
where n is a positive integer and are real numbers and
Setting the polynomial equal to zero gives a polynomial equation . The total number of solutions (real and complex) to a polynomial equation is equal to the highest exponent n .
Solve the polynomial by factoring:
First, set the equation equal to zero. Then factor out what is common to both terms, the GCF.
Notice that we have the difference of squares in the factor which we will continue to factor and obtain two solutions. The first term, generates, technically, two solutions as the exponent is 2, but they are the same solution.
The solutions are and
Solve a polynomial by grouping:
This polynomial consists of 4 terms, which we can solve by grouping. Grouping procedures require factoring the first two terms and then factoring the last two terms. If the factors in the parentheses are identical, we can continue the process and solve, unless more factoring is suggested.
The grouping process ends here, as we can factor using the difference of squares formula.
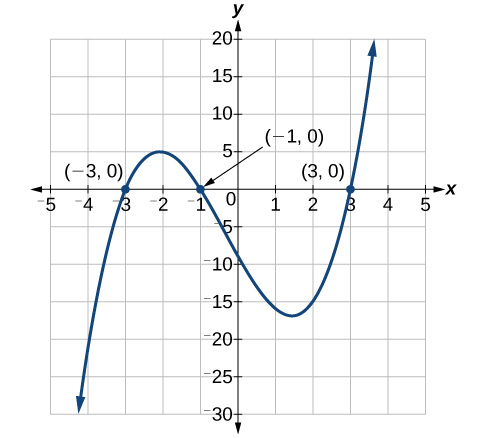
The solutions are and Note that the highest exponent is 3 and we obtained 3 solutions. We can see the solutions, the x- intercepts, on the graph in [link] .
Radical equations are equations that contain variables in the radicand (the expression under a radical symbol), such as
Radical equations may have one or more radical terms, and are solved by eliminating each radical, one at a time. We have to be careful when solving radical equations, as it is not unusual to find extraneous solutions , roots that are not, in fact, solutions to the equation. These solutions are not due to a mistake in the solving method, but result from the process of raising both sides of an equation to a power. However, checking each answer in the original equation will confirm the true solutions.
An equation containing terms with a variable in the radicand is called a radical equation .
Given a radical equation, solve it.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Algebra and trigonometry' conversation and receive update notifications?