| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

Discovered by Benoit Mandelbrot around 1980, the Mandelbrot Set is one of the most recognizable fractal images. The image is built on the theory of self-similarity and the operation of iteration. Zooming in on a fractal image brings many surprises, particularly in the high level of repetition of detail that appears as magnification increases. The equation that generates this image turns out to be rather simple.
In order to better understand it, we need to become familiar with a new set of numbers. Keep in mind that the study of mathematics continuously builds upon itself. Negative integers, for example, fill a void left by the set of positive integers. The set of rational numbers, in turn, fills a void left by the set of integers. The set of real numbers fills a void left by the set of rational numbers. Not surprisingly, the set of real numbers has voids as well. In this section, we will explore a set of numbers that fills voids in the set of real numbers and find out how to work within it.
We know how to find the square root of any positive real number. In a similar way, we can find the square root of any negative number. The difference is that the root is not real. If the value in the radicand is negative, the root is said to be an imaginary number . The imaginary number is defined as the square root of
So, using properties of radicals,
We can write the square root of any negative number as a multiple of Consider the square root of
We use and not because the principal root of is the positive root.
A complex number is the sum of a real number and an imaginary number. A complex number is expressed in standard form when written where is the real part and is the imaginary part. For example, is a complex number. So, too, is
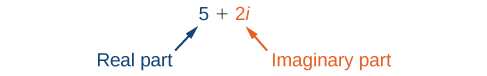
Imaginary numbers differ from real numbers in that a squared imaginary number produces a negative real number. Recall that when a positive real number is squared, the result is a positive real number and when a negative real number is squared, the result is also a positive real number. Complex numbers consist of real and imaginary numbers.
A complex number is a number of the form where
If then is a real number. If and is not equal to 0, the complex number is called a pure imaginary number. An imaginary number is an even root of a negative number.
Given an imaginary number, express it in the standard form of a complex number.
Express in standard form.
In standard form, this is
We cannot plot complex numbers on a number line as we might real numbers. However, we can still represent them graphically. To represent a complex number, we need to address the two components of the number. We use the complex plane , which is a coordinate system in which the horizontal axis represents the real component and the vertical axis represents the imaginary component. Complex numbers are the points on the plane, expressed as ordered pairs where represents the coordinate for the horizontal axis and represents the coordinate for the vertical axis.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Algebra and trigonometry' conversation and receive update notifications?