| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Graph the parametric equations and and the rectangular equivalent on the same coordinate system.
Construct a table of values for the parametric equations, as we did in the previous example, and graph on the same grid, as in [link] .
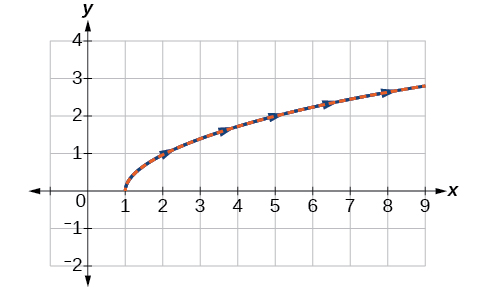
Sketch the graph of the parametric equations along with the rectangular equation on the same grid.
The graph of the parametric equations is in red and the graph of the rectangular equation is drawn in blue dots on top of the parametric equations.
Many of the advantages of parametric equations become obvious when applied to solving real-world problems. Although rectangular equations in x and y give an overall picture of an object's path, they do not reveal the position of an object at a specific time. Parametric equations, however, illustrate how the values of x and y change depending on t , as the location of a moving object at a particular time.
A common application of parametric equations is solving problems involving projectile motion. In this type of motion, an object is propelled forward in an upward direction forming an angle of to the horizontal, with an initial speed of and at a height above the horizontal.
The path of an object propelled at an inclination of to the horizontal, with initial speed and at a height above the horizontal, is given by
where accounts for the effects of gravity and is the initial height of the object. Depending on the units involved in the problem, use or The equation for gives horizontal distance, and the equation for gives the vertical distance.
Given a projectile motion problem, use parametric equations to solve.
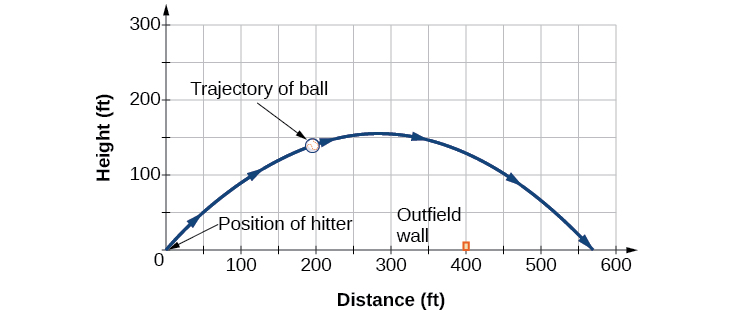
Solve the problem presented at the beginning of this section. Does the batter hit the game-winning home run? Assume that the ball is hit with an initial velocity of 140 feet per second at an angle of to the horizontal, making contact 3 feet above the ground.
Use the formulas to set up the equations. The horizontal position is found using the parametric equation for Thus,
The vertical position is found using the parametric equation for Thus,
Substitute 2 into the equations to find the horizontal and vertical positions of the ball.
After 2 seconds, the ball is 198 feet away from the batter’s box and 137 feet above the ground.
To calculate how long the ball is in the air, we have to find out when it will hit ground, or when Thus,
When seconds, the ball has hit the ground. (The quadratic equation can be solved in various ways, but this problem was solved using a computer math program.)
We cannot confirm that the hit was a home run without considering the size of the outfield, which varies from field to field. However, for simplicity’s sake, let’s assume that the outfield wall is 400 feet from home plate in the deepest part of the park. Let’s also assume that the wall is 10 feet high. In order to determine whether the ball clears the wall, we need to calculate how high the ball is when x = 400 feet. So we will set x = 400, solve for and input into
The ball is 141.8 feet in the air when it soars out of the ballpark. It was indeed a home run. See [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Algebra and trigonometry' conversation and receive update notifications?