| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
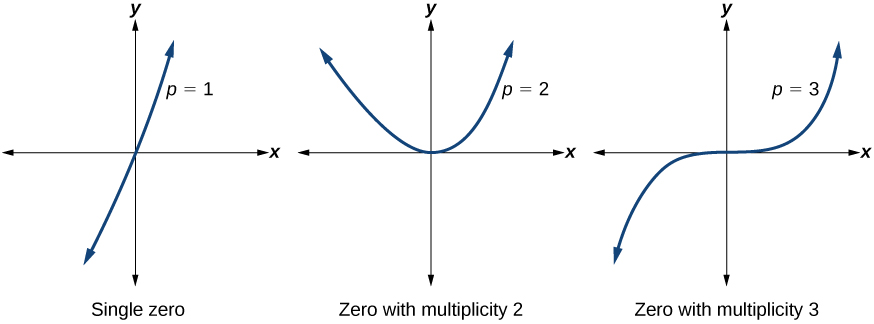
The x -intercept is the repeated solution of equation The graph touches the axis at the intercept and changes direction. The factor is quadratic (degree 2), so the behavior near the intercept is like that of a quadratic—it bounces off of the horizontal axis at the intercept.
The factor is repeated, that is, the factor appears twice. The number of times a given factor appears in the factored form of the equation of a polynomial is called the multiplicity . The zero associated with this factor, has multiplicity 2 because the factor occurs twice.
The x -intercept is the repeated solution of factor The graph passes through the axis at the intercept, but flattens out a bit first. This factor is cubic (degree 3), so the behavior near the intercept is like that of a cubic—with the same S-shape near the intercept as the toolkit function We call this a triple zero, or a zero with multiplicity 3.
For zeros with even multiplicities, the graphs touch or are tangent to the x -axis. For zeros with odd multiplicities, the graphs cross or intersect the x -axis. See [link] for examples of graphs of polynomial functions with multiplicity 1, 2, and 3.
For higher even powers, such as 4, 6, and 8, the graph will still touch and bounce off of the horizontal axis but, for each increasing even power, the graph will appear flatter as it approaches and leaves the x -axis.
For higher odd powers, such as 5, 7, and 9, the graph will still cross through the horizontal axis, but for each increasing odd power, the graph will appear flatter as it approaches and leaves the x -axis.
If a polynomial contains a factor of the form the behavior near the intercept is determined by the power We say that is a zero of multiplicity
The graph of a polynomial function will touch the x -axis at zeros with even multiplicities. The graph will cross the x -axis at zeros with odd multiplicities.
The sum of the multiplicities is the degree of the polynomial function.
Given a graph of a polynomial function of degree identify the zeros and their multiplicities.
Use the graph of the function of degree 6 in [link] to identify the zeros of the function and their possible multiplicities.
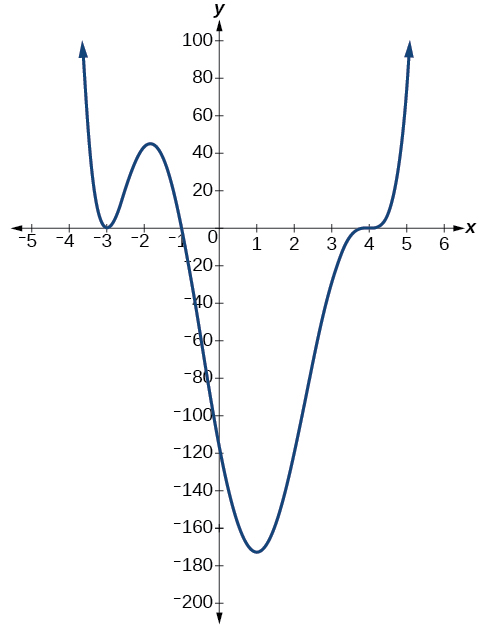
The polynomial function is of degree 6. The sum of the multiplicities must be 6.
Starting from the left, the first zero occurs at The graph touches the x -axis, so the multiplicity of the zero must be even. The zero of most likely has multiplicity
The next zero occurs at The graph looks almost linear at this point. This is a single zero of multiplicity 1.
The last zero occurs at The graph crosses the x -axis, so the multiplicity of the zero must be odd. We know that the multiplicity is likely 3 and that the sum of the multiplicities is 6.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Algebra and trigonometry' conversation and receive update notifications?