| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Access the list of equations.
![]()
Select each equal sign (=).
![]()
![]()
![]()
Access the list of equations.
![]()
Use the arrow keys to navigate to the right of each equal sign (=) and clear them.
![]()
![]()
![]()
Access the ZOOM menu.
![]()
Select
<9:ZoomStat> .
![]()
Access graphing mode.
![]() ,
,
[STAT PLOT]
Select
<1:Plot 1> to access the first graph.
![]()
Use the arrows to select
<ON> and turn on Plot 1.
![]()
Use the arrows to select the box plot picture and enable it.
![]()
<Xlist> .If "L1" is not selected, select it.
![]() ,
,
[L1] ,
![]()
<Freq> .Indicate that the frequencies are in
[L2] .
![]() ,
,
[L2] ,
![]()
Go back to access other graphs.
![]() ,
,
[STAT PLOT]
View the box plot.
![]() ,
,
[STAT PLOT]
The following data is real. The percent of declared ethnic minority students at De Anza College for selected years from 1970–1995 was:
| Year | Student Ethnic Minority Percentage |
|---|---|
| 1970 | 14.13 |
| 1973 | 12.27 |
| 1976 | 14.08 |
| 1979 | 18.16 |
| 1982 | 27.64 |
| 1983 | 28.72 |
| 1986 | 31.86 |
| 1989 | 33.14 |
| 1992 | 45.37 |
| 1995 | 53.1 |
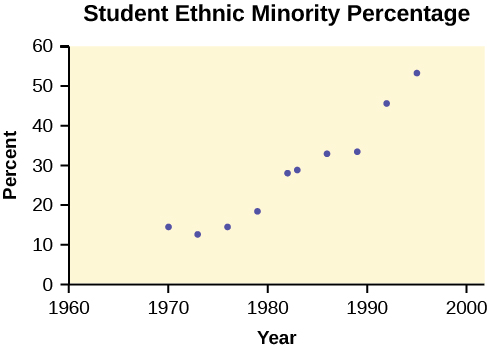
The TI-83 has a built-in linear regression feature, which allows the data to be edited.The
x -values will be in
[L1] ; the
y -values in
[L2] .
ON Turns calculator on.
![]()
Access graphing mode.
![]() ,
,
[STAT PLOT]
Turn off all plots.
![]() ,
,
![]()
Access the mode menu.
![]() ,
,
[STAT PLOT]
Navigate to
<Float> and then to the right to
<3> .
![]()
![]()
All numbers will be rounded to three decimal places until changed.
![]()
Enter statistics mode and clear lists
[L1] and
[L2] , as describe previously.
![]() ,
,
![]()
Enter editing mode to insert values for
x and
y .
![]() ,
,
![]()
Access the catalog.
![]() ,
,
[CATALOG]
Arrow down and select
<DiagnosticOn>
![]() ... ,
... ,
![]() ,
,
![]()
Access linear regression.
![]()
![]()
Select the form of
y =
a +
bx .
![]() ,
,
![]()
The display will show:
This means the Line of Best Fit (Least Squares Line) is:
Access graphing mode.
![]() ,
,
[STAT PLOT]
Select
<1:plot 1> To access plotting - first graph.
![]()
Navigate and select
<ON> to turn on Plot 1.
<ON>
![]()
Select the scatter plot.
![]()
<Xlist> .[L1] is not selected, press
[L1] to select it.Confirm that the data values are in
[L1] .
<ON>
![]()
<Ylist> .Select that the frequencies are in
[L2] .
![]() ,
,
[L2] ,
![]()
Go back to access other graphs.
![]() ,
,
[STAT PLOT]

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introductory statistics' conversation and receive update notifications?