| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
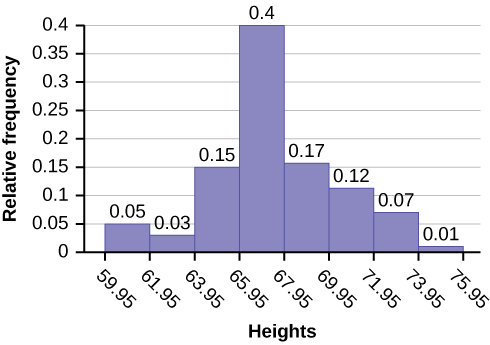
The smallest data value is 60. Since the data with the most decimal places has one decimal (for instance, 61.5), we want our starting point to have two decimal places. Since the numbers 0.5, 0.05, 0.005, etc. are convenient numbers, use 0.05 and subtract it from 60, the smallest value, for the convenient starting point.
60 – 0.05 = 59.95 which is more precise than, say, 61.5 by one decimal place. The starting point is, then, 59.95.
The largest value is 74, so 74 + 0.05 = 74.05 is the ending value.
Next, calculate the width of each bar or class interval. To calculate this width, subtract the starting point from the ending value and divide by the number of bars (you must choose the number of bars you desire). Suppose you choose eight bars.
We will round up to two and make each bar or class interval two units wide. Rounding up to two is one way to prevent a value from falling on a boundary. Rounding to the next number is often necessary even if it goes against the standard rules of rounding. For this example, using 1.76 as the width would also work. A guideline that is followed by some for the width of a bar or class interval is to take the square root of the number of data values and then round to the nearest whole number, if necessary. For example, if there are 150 values of data, take the square root of 150 and round to 12 bars or intervals.
The boundaries are:
The heights 60 through 61.5 inches are in the interval 59.95–61.95. The heights that are 63.5 are in the interval 61.95–63.95. The heights that are 64 through 64.5 are in the interval 63.95–65.95. The heights 66 through 67.5 are in the interval 65.95–67.95. The heights 68 through 69.5 are in the interval 67.95–69.95. The heights 70 through 71 are in the interval 69.95–71.95. The heights 72 through 73.5 are in the interval 71.95–73.95. The height 74 is in the interval 73.95–75.95.
The following histogram displays the heights on the x -axis and relative frequency on the y -axis.
The following data are the shoe sizes of 50 male students. The sizes are continuous data since shoe size is measured. Construct a histogram and calculate the width of each bar or class interval. Suppose you choose six bars.
9; 9; 9.5; 9.5; 10; 10; 10; 10; 10; 10; 10.5; 10.5; 10.5; 10.5; 10.5; 10.5; 10.5; 10.5
11; 11; 11; 11; 11; 11; 11; 11; 11; 11; 11; 11; 11; 11.5; 11.5; 11.5; 11.5; 11.5; 11.5; 11.5
12; 12; 12; 12; 12; 12; 12; 12.5; 12.5; 12.5; 12.5; 14
Smallest value: 9
Largest value: 14
Convenient starting value: 9 – 0.05 = 8.95
Convenient ending value: 14 + 0.05 = 14.05
The calculations suggests using 0.85 as the width of each bar or class interval. You can also use an interval with a width equal to one.
The following data are the number of books bought by 50 part-time college students at ABC College. The number of books is
discrete data , since books are counted.
1; 1; 1; 1; 1; 1; 1; 1; 1; 1; 1
2; 2; 2; 2; 2; 2; 2; 2; 2; 2
3; 3; 3; 3; 3; 3; 3; 3; 3; 3; 3; 3; 3; 3; 3; 3
4; 4; 4; 4; 4; 4
5; 5; 5; 5; 5
6; 6
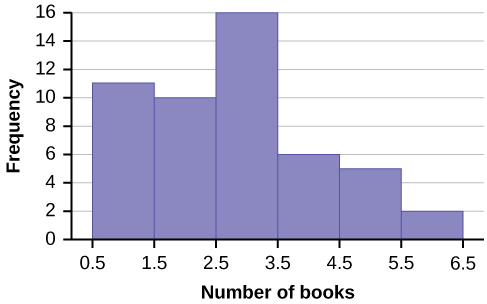
Eleven students buy one book. Ten students buy two books. Sixteen students buy three books. Six students buy four books. Five students buy five books. Two students buy six books.
Because the data are integers, subtract 0.5 from 1, the smallest data value and add 0.5 to 6, the largest data value. Then the starting point is 0.5 and the ending value is 6.5.
Next, calculate the width of each bar or class interval. If the data are discrete and there are not too many different values, a width that places the data values in the middle of the bar or class interval is the most convenient. Since the data consist of the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and the starting point is 0.5, a width of one places the 1 in the middle of the interval from 0.5 to 1.5, the 2 in the middle of the interval from 1.5 to 2.5, the 3 in the middle of the interval from 2.5 to 3.5, the 4 in the middle of the interval from _______ to _______, the 5 in the middle of the interval from _______ to _______, and the _______ in the middle of the interval from _______ to _______ .
Calculate the number of bars as follows:
where 1 is the width of a bar. Therefore, bars = 6.
The following histogram displays the number of books on the x -axis and the frequency on the y -axis.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introductory statistics' conversation and receive update notifications?