| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
If we have biological rhythms, then is there some sort of biological clock ? In the brain, the hypothalamus, which lies above the pituitary gland, is a main center of homeostasis. Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a balance, or optimal level, within a biological system.
The brain’s clock mechanism is located in an area of the hypothalamus known as the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) . The axons of light-sensitive neurons in the retina provide information to the SCN based on the amount of light present, allowing this internal clock to be synchronized with the outside world (Klein, Moore,&Reppert, 1991; Welsh, Takahashi,&Kay, 2010) ( [link] ).
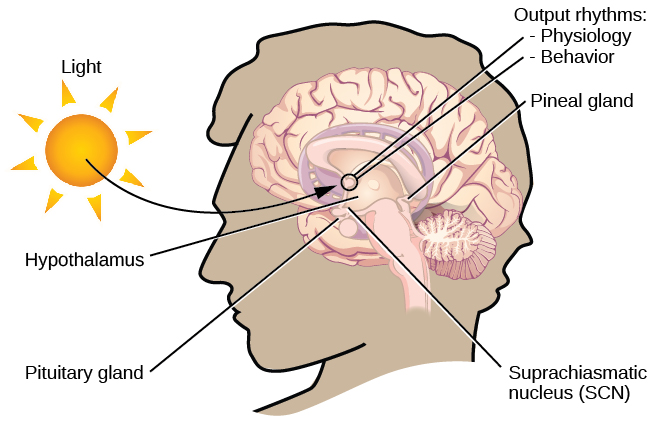
Generally, and for most people, our circadian cycles are aligned with the outside world. For example, most people sleep during the night and are awake during the day. One important regulator of sleep-wake cycles is the hormone melatonin . The pineal gland , an endocrine structure located inside the brain that releases melatonin, is thought to be involved in the regulation of various biological rhythms and of the immune system during sleep (Hardeland, Pandi-Perumal,&Cardinali, 2006). Melatonin release is stimulated by darkness and inhibited by light.
There are individual differences with regards to our sleep-wake cycle. For instance, some people would say they are morning people, while others would consider themselves to be night owls. These individual differences in circadian patterns of activity are known as a person’s chronotype, and research demonstrates that morning larks and night owls differ with regard to sleep regulation (Taillard, Philip, Coste, Sagaspe,&Bioulac, 2003). Sleep regulation refers to the brain’s control of switching between sleep and wakefulness as well as coordinating this cycle with the outside world.
Watch this brief video describing circadian rhythms and how they affect sleep.
Whether lark, owl, or somewhere in between, there are situations in which a person’s circadian clock gets out of synchrony with the external environment. One way that this happens involves traveling across multiple time zones. When we do this, we often experience jet lag. Jet lag is a collection of symptoms that results from the mismatch between our internal circadian cycles and our environment. These symptoms include fatigue, sluggishness, irritability, and insomnia (i.e., a consistent difficulty in falling or staying asleep for at least three nights a week over a month’s time) (Roth, 2007).
Individuals who do rotating shift work are also likely to experience disruptions in circadian cycles. Rotating shift work refers to a work schedule that changes from early to late on a daily or weekly basis. For example, a person may work from 7:00 a.m. to 3:00 p.m. on Monday, 3:00 a.m. to 11:00 a.m. on Tuesday, and 11:00 a.m. to 7:00 p.m. on Wednesday. In such instances, the individual’s schedule changes so frequently that it becomes difficult for a normal circadian rhythm to be maintained. This often results in sleeping problems, and it can lead to signs of depression and anxiety. These kinds of schedules are common for individuals working in health care professions and service industries, and they are associated with persistent feelings of exhaustion and agitation that can make someone more prone to making mistakes on the job (Gold et al., 1992; Presser, 1995).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?