| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
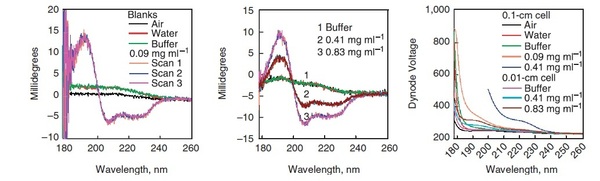
Most of proteins and peptides will require using buffers in order to prevent denaturation. Caution should be shown to avoid using any optically active buffers. Clear solutions are required. CD is taken in high transparency quartz cuvettes to ensure least interference. There are cuvettes available that have path-length ranging from 0.01 cm to 1 cm. Depending on UV activity of buffers used one should choose a cuvette with path-length (distance the beam of light passes through the sample) that compensates for UV absorbance of buffer. Solutions should be prepared according to cuvette that will be used, see [link] .
| Cuvette path (cm) | Concentration of sample (mg/mL) |
| 0.01 - 0.02 | 0.2 – 1.0 |
| 0.1 | 0.05 – 0.2 |
| 1 | 0.005 – 0.01 |
Besides, just like salts used to prepare pallets in FT-IR, the buffers in CD will show cutoffs at a certain point in low wavelength region, meaning that buffers start to absorb after certain wavelengh. The cutoff values for most of common buffers are known and can be found from manufacturer. Oxygen absorbs light below 200 nm. Therefore, in order to remove interference buffers should be prepared from distilled water or the water should be degassed before use. Another important point is to accurately determine concentration of sample, because concentration should be known for CD data analysis. Concentration of sample can be determined from extinction coefficients, if such are reported in literature also for protein samples quantitative amino acid analysis can be used.
Many CD instrument come bundled with a sample compartment temperature control unit. This is very handy when doing stability and unfolding/denaturation studies of proteins. Check to make sure the heat sink is filled with water. Turn the temperature control unit on and set to chosen temperature.
UV source in CD is very powerful lamp and can generates large amounts of Ozone in its chamber. Ozone significantly reduces the life of the lamp. Therefore, oxygen should be removed before turning on the main lamp (otherwise it will be converted to ozone near lamp). For this purpose nitrogen gas is constantly flushed into lamp compartment. Let Nitrogen flush at least for 15 min. before turning on the lamp.
After saving the data for both the spectra of the sample and blank is smoothed using built-in commands of controller software. The smoothed baseline is subtracted from the smoothed spectrum of the sample. The next step is to use software bundles which have algorithms for estimating secondary structure of proteins. Input the data into the software package of choice and process it. The output from algorithms will be the percentage of a particular secondary structure conformation in sample. The data shown in [link] lists commonly used methods and comparers them for several proteins. The estimated secondary structure is compared to X-ray data, and one can see that it is best to use several methods for best accuracy.

What advantages CD has over other analysis methods? CD spectroscopy is an excellent, rapid method for assessing the secondary structure of proteins and performing studies of dynamic systems like folding and binding of proteins. It worth noting that CD does not provide information about the position of those subunits with specific conformation. However, CD outrivals other techniques in rapid assessing of the structure of unknown protein samples and in monitoring structural changes of known proteins caused by ligation and complex formation, temperature change, mutations, denaturants. CD is also widely used to juxtapose fused proteins with wild type counterparts, because CD spectra can tell whether the fused protein retained the structure of wild type or underwent changes.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?