| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A popular and powerful tool in the chemical world, chromatography separates mixtures based on chemical properties – even some than were previously thought inseparable. It combines a multitude of pieces, concepts, and chemicals to form an instrument suited to specific separation. One form of chromatography that is often overlooked is that of supercritical fluid chromatography.
Supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) begins its history in 1962 under the name “high pressure gas chromatography”. It started off slow and was quickly overshadowed by the development of high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and the already developed gas chromatography. SFC was not a popular method of chromatography until the late 1980s, when more publications began exemplifying its uses and techniques.
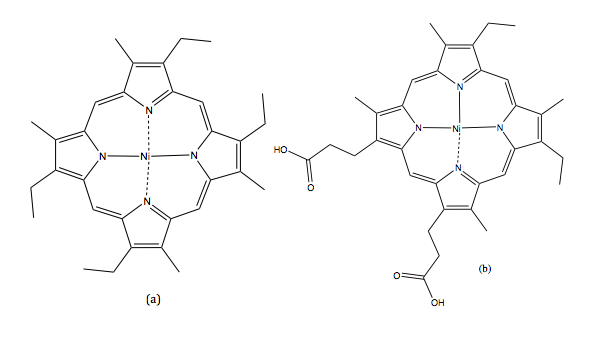
SFC was first reported by Klesper et al. They succeeded in separating thermally labile porphyrin mixtures on polyethylene glycol stationary phase with two mobile phase units: dichlorodifluoromethane (CCl 2 F 2 ) and monochlorodifluoromethane (CHCl 2 F), as shown in [link] . Their results proved that supercritical fluids’ low viscosity but high diffusivity functions well as a mobile phase.
After Klesper’s paper detailing his separation procedure, subsequent scientists aimed to find the perfect mobile phase and the possible uses for SFC. Using gases such as He, N 2 , CO 2 , and NH 3 , they examined purines, nucleotides, steroids, sugars, terpenes, amino acids, proteins, and many more substances for their retention behavior. They discovered that CO 2 was an ideal supercritical fluid due to its low critical temperature of 31 °C and relatively low critical pressure of 72.8 atm. Extra advantages of CO 2 included it being cheap, non-flammable, and non-toxic. CO 2 is now the standard mobile phase for SFC.
In the development of SFC over the years, the technique underwent multiple trial-and-error phases. Open tubular capillary column SFC had the advantage of independently and cooperatively changing all three parameters (pressure, temperature, and modifier content) to a certain extent. Like any chromatography method, however, it had its drawbacks. Changing the pressure, the most important parameter, often required changing the flow velocity due to the constant diameter of the capillaries. Additionally, CO 2 , the ideal mobile phase, is non-polar, and its polarity could not be altered easily or with a gradient.
Over the years, many uses were discovered for SFC. It was identified as a useful tool in the separation of chiral compounds, drugs, natural products, and organometallics (see below for more detail). Most SFCs currently are involved a silica (or silica + modifier) packed column with a CO 2 (or CO 2 + modifier) mobile phase. Mass spectrometry is the most common tool used to analyze the separated samples.
As mentioned previously, the advantage to supercritical fluids is the combination of the useful properties from two phases: liquids and gases. Supercritical fluids are gas-like in the ways of expanding to fill a given volume, and the motions of the particles are close to that of a gas. On the side of liquid properties, supercritical fluids have densities near that of liquids and thus dissolve and interact with other particles, as you would expect of a liquid. To visualize phase changes in relation to pressure and temperature, phase diagrams are used as shown in [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?