| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Imagine a vendor carrying a basket of vegetables on her head. Is she doing any work? One would definitely say yes! However, in Physics she is not doing any work! Again, imagine a boy pushing against a wall? Is he doing any work? We can see that his muscles are contracting and expanding. He may even be sweating. But in Physics, he is not doing any work!
If the vendor is carrying a very heavy load for a long distance, we would say she has lot of energy. By this, we mean that she has a lot of stamina. If a car can travel very fast, we describe the car as powerful. So, there is a link between power and speed. However, power means something different in Physics. This chapter describes the links between work, energy and power and what these mean in Physics.
You will learn that work and energy are closely related. You shall see that the energy of an object is its capacity to do work and doing work is the process of transferring energy from one object or form to another. In other words,
Lifting objects or throwing them requires that you do work on them. Even making electricity flow requires that something do work. Something must have energy and transfer it through doing work to make things happen.
When a force exerted on an object causes it to move, work is done on the object (except if the force and displacement are at right angles to each other).
This means that in order for work to be done, an object must be moved a distance by a force , such that there is some non-zero component of the force in the direction of the displacement. Work is calculated as:
where is the applied force, is the displacement of the object and is the angle between the applied force and the direction of motion.
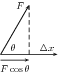
It is very important to note that for work to be done there must be a component of the applied force in the direction of motion. Forces perpendicular to the direction of motion do no work.
For example work is done on the object in [link] ,
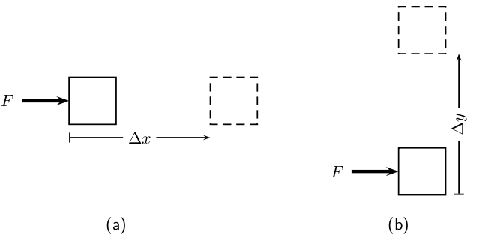
Decide whether on not work is done in the following situations. Remember that for work to be done a force must be applied in the direction of motion and there must be a displacement. Give reasons for your answer.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 12 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?