| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The circuits and components we have discussed are very useful. You can build a radio or television with them. You can make a telephone. Even if that was all there was to electronics, it would still be very useful. However, the great breakthrough in the last fifty years or so has been in digital electronics. This is the subject which gave us the computer. The computer has revolutionized the way business, engineering and science are done. Small computers programmed to do a specific job (called microprocessors) are now used in almost every electronic machine from cars to washing machines. Computers have also changed the way we communicate. We used to have telegraph or telephone wires passing up and down a country — each one carrying one telephone call or signal. We now have optic fibres each capable of carrying tens of thousands of telephone calls using digital signals.
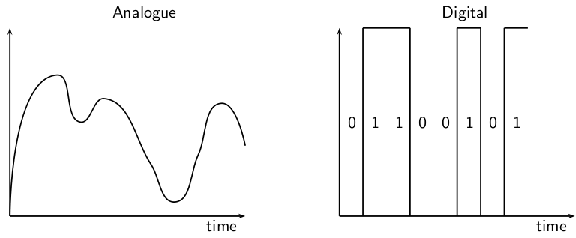
So, what is a digital signal? Look at [link] . A normal signal, called an analogue signal, carries a smooth wave. At any time, the voltage of the signal could take any value. It could be 2,00 V or 3,53 V or anything else. A digital signal can only take certain voltages. The simplest case is shown in the figure — the voltage takes one of two values. It is either high , or it is low . It never has any other value.
These two special voltages are given symbols. The low voltage level is written 0, while the high voltage level is written as 1. When you send a digital signal, you set the voltage you want (0 or 1), then keep this fixed for a fixed amount of time (for example 0.01 s), then you send the next 0 or 1. The digital signal in [link] could be written 01100101.
Why are digital signals so good?
The simplest digital circuits are called logic gates . Each logic gate makes a decision based on the information it receives. Different logic gates are set up to make the decisions in different ways. Each logic gate will be made of many microscopic transistors connected together within a thin wafer of silicon. This tiny circuit is called an Integrated Circuit or I.C. - all the parts are in one place (integrated) on the silicon wafer.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 12 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?