| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
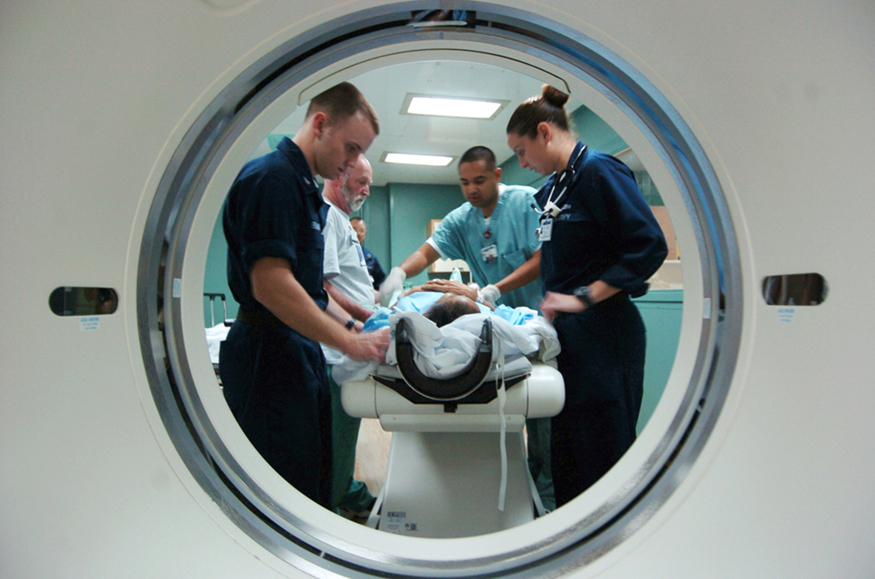
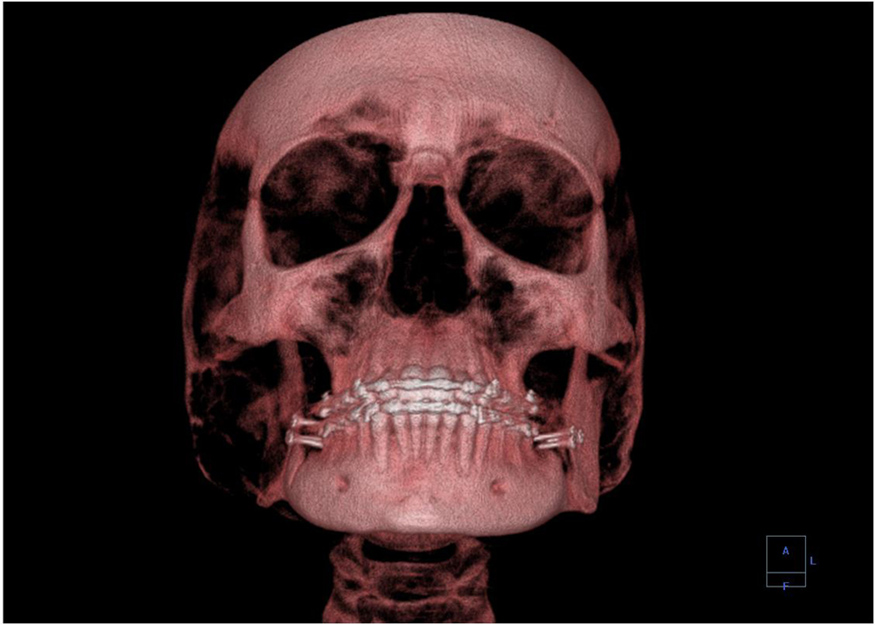
A standard x ray gives only a two-dimensional view of the object. Dense bones might hide images of soft tissue or organs. If you took another x ray from the side of the person (the first one being from the front), you would gain additional information. While shadow images are sufficient in many applications, far more sophisticated images can be produced with modern technology. [link] shows the use of a computed tomography (CT) scanner, also called computed axial tomography (CAT) scanner. X rays are passed through a narrow section (called a slice) of the patient’s body (or body part) over a range of directions. An array of many detectors on the other side of the patient registers the x rays. The system is then rotated around the patient and another image is taken, and so on. The x-ray tube and detector array are mechanically attached and so rotate together. Complex computer image processing of the relative absorption of the x rays along different directions produces a highly-detailed image. Different slices are taken as the patient moves through the scanner on a table. Multiple images of different slices can also be computer analyzed to produce three-dimensional information, sometimes enhancing specific types of tissue, as shown in [link] . G. Hounsfield (UK) and A. Cormack (US) won the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1979 for their development of computed tomography.
Since x-ray photons are very energetic, they have relatively short wavelengths. For example, the 54.4-keV x ray of [link] has a wavelength . Thus, typical x-ray photons act like rays when they encounter macroscopic objects, like teeth, and produce sharp shadows; however, since atoms are on the order of 0.1 nm in size, x rays can be used to detect the location, shape, and size of atoms and molecules. The process is called x-ray diffraction , because it involves the diffraction and interference of x rays to produce patterns that can be analyzed for information about the structures that scattered the x rays. Perhaps the most famous example of x-ray diffraction is the discovery of the double-helix structure of DNA in 1953 by an international team of scientists working at the Cavendish Laboratory—American James Watson, Englishman Francis Crick, and New Zealand–born Maurice Wilkins. Using x-ray diffraction data produced by Rosalind Franklin, they were the first to discern the structure of DNA that is so crucial to life. For this, Watson, Crick, and Wilkins were awarded the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. There is much debate and controversy over the issue that Rosalind Franklin was not included in the prize.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?