| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
which is nearly identical to the mass of a hydrogen atom. What Thomson and Millikan had done was to prove the existence of one substructure of atoms, the electron, and further to show that it had only a tiny fraction of the mass of an atom. The nucleus of an atom contains most of its mass, and the nature of the nucleus was completely unanticipated.
Another important characteristic of quantum mechanics was also beginning to emerge. All electrons are identical to one another. The charge and mass of electrons are not average values; rather, they are unique values that all electrons have. This is true of other fundamental entities at the submicroscopic level. All protons are identical to one another, and so on.
Here, we examine the first direct evidence of the size and mass of the nucleus. In later chapters, we will examine many other aspects of nuclear physics, but the basic information on nuclear size and mass is so important to understanding the atom that we consider it here.
Nuclear radioactivity was discovered in 1896, and it was soon the subject of intense study by a number of the best scientists in the world. Among them was New Zealander Lord Ernest Rutherford, who made numerous fundamental discoveries and earned the title of “father of nuclear physics.” Born in Nelson, Rutherford did his postgraduate studies at the Cavendish Laboratories in England before taking up a position at McGill University in Canada where he did the work that earned him a Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1908. In the area of atomic and nuclear physics, there is much overlap between chemistry and physics, with physics providing the fundamental enabling theories. He returned to England in later years and had six future Nobel Prize winners as students. Rutherford used nuclear radiation to directly examine the size and mass of the atomic nucleus. The experiment he devised is shown in [link] . A radioactive source that emits alpha radiation was placed in a lead container with a hole in one side to produce a beam of alpha particles, which are a type of ionizing radiation ejected by the nuclei of a radioactive source. A thin gold foil was placed in the beam, and the scattering of the alpha particles was observed by the glow they caused when they struck a phosphor screen.
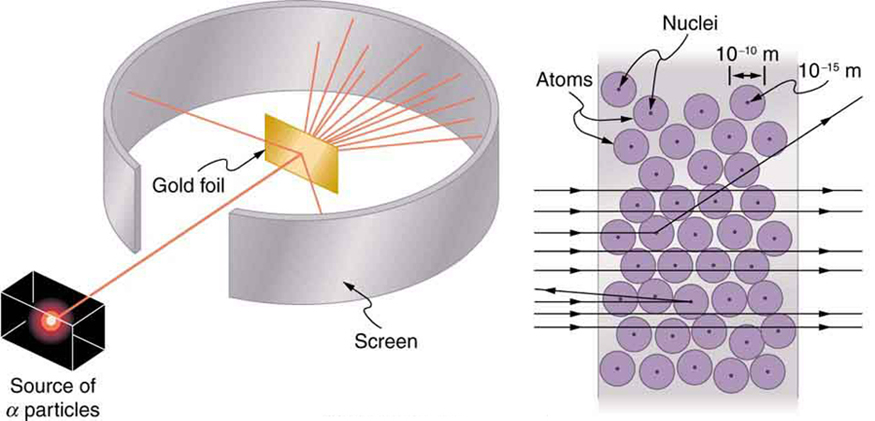
Alpha particles were known to be the doubly charged positive nuclei of helium atoms that had kinetic energies on the order of when emitted in nuclear decay, which is the disintegration of the nucleus of an unstable nuclide by the spontaneous emission of charged particles. These particles interact with matter mostly via the Coulomb force, and the manner in which they scatter from nuclei can reveal nuclear size and mass. This is analogous to observing how a bowling ball is scattered by an object you cannot see directly. Because the alpha particle’s energy is so large compared with the typical energies associated with atoms ( versus ), you would expect the alpha particles to simply crash through a thin foil much like a supersonic bowling ball would crash through a few dozen rows of bowling pins. Thomson had envisioned the atom to be a small sphere in which equal amounts of positive and negative charge were distributed evenly. The incident massive alpha particles would suffer only small deflections in such a model. Instead, Rutherford and his collaborators found that alpha particles occasionally were scattered to large angles, some even back in the direction from which they came! Detailed analysis using conservation of momentum and energy—particularly of the small number that came straight back—implied that gold nuclei are very small compared with the size of a gold atom, contain almost all of the atom’s mass, and are tightly bound. Since the gold nucleus is several times more massive than the alpha particle, a head-on collision would scatter the alpha particle straight back toward the source. In addition, the smaller the nucleus, the fewer alpha particles that would hit one head on.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?