| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
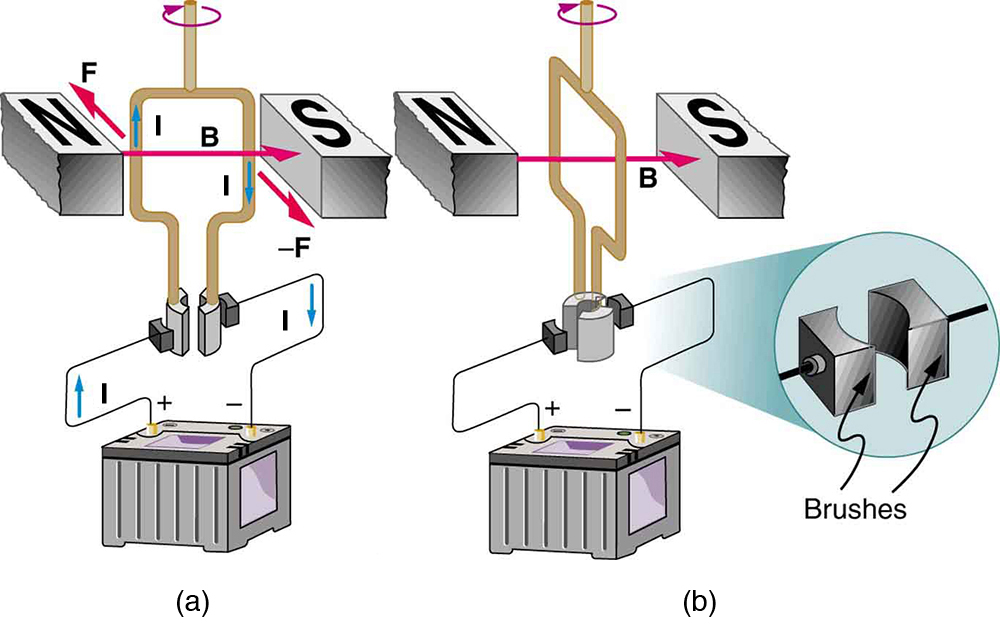
The torque found in the preceding example is the maximum. As the coil rotates, the torque decreases to zero at . The torque then reverses its direction once the coil rotates past . (See [link] (d).) This means that, unless we do something, the coil will oscillate back and forth about equilibrium at . To get the coil to continue rotating in the same direction, we can reverse the current as it passes through with automatic switches called brushes . (See [link] .)
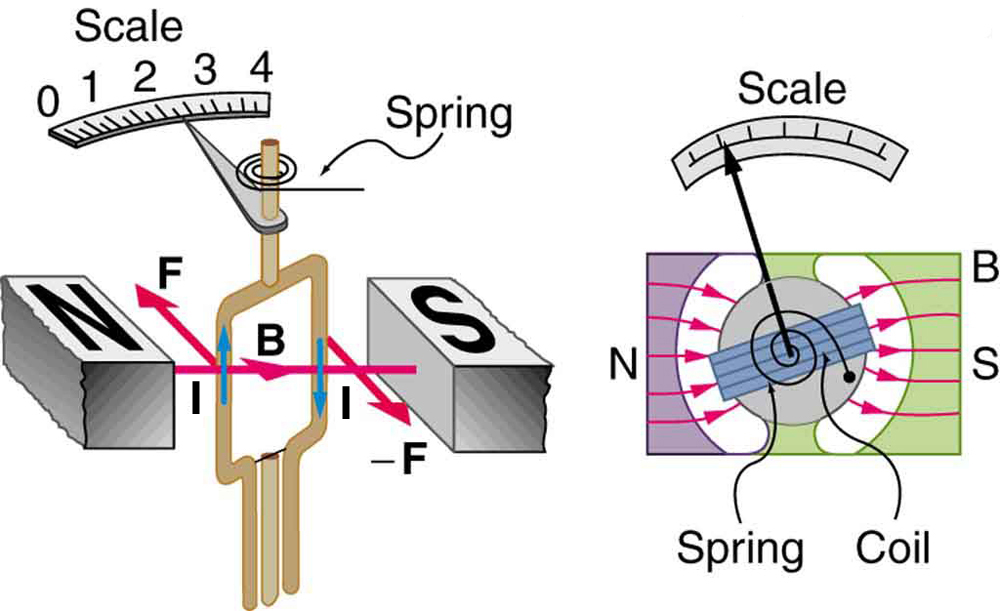
Meters , such as those in analog fuel gauges on a car, are another common application of magnetic torque on a current-carrying loop. [link] shows that a meter is very similar in construction to a motor. The meter in the figure has its magnets shaped to limit the effect of by making perpendicular to the loop over a large angular range. Thus the torque is proportional to and not . A linear spring exerts a counter-torque that balances the current-produced torque. This makes the needle deflection proportional to . If an exact proportionality cannot be achieved, the gauge reading can be calibrated. To produce a galvanometer for use in analog voltmeters and ammeters that have a low resistance and respond to small currents, we use a large loop area , high magnetic field , and low-resistance coils.
Draw a diagram and use RHR-1 to show that the forces on the top and bottom segments of the motor’s current loop in [link] are vertical and produce no torque about the axis of rotation.
(a) By how many percent is the torque of a motor decreased if its permanent magnets lose 5.0% of their strength? (b) How many percent would the current need to be increased to return the torque to original values?
(a) decreases by 5.00% if B decreases by 5.00%
(b) 5.26% increase
(a) What is the maximum torque on a 150-turn square loop of wire 18.0 cm on a side that carries a 50.0-A current in a 1.60-T field? (b) What is the torque when is
Find the current through a loop needed to create a maximum torque of The loop has 50 square turns that are 15.0 cm on a side and is in a uniform 0.800-T magnetic field.
10.0 A
Calculate the magnetic field strength needed on a 200-turn square loop 20.0 cm on a side to create a maximum torque of if the loop is carrying 25.0 A.
Since the equation for torque on a current-carrying loop is , the units of must equal units of . Verify this.
.
(a) At what angle is the torque on a current loop 90.0% of maximum? (b) 50.0% of maximum? (c) 10.0% of maximum?
A proton has a magnetic field due to its spin on its axis. The field is similar to that created by a circular current loop in radius with a current of (no kidding). Find the maximum torque on a proton in a 2.50-T field. (This is a significant torque on a small particle.)
(a) A 200-turn circular loop of radius 50.0 cm is vertical, with its axis on an east-west line. A current of 100 A circulates clockwise in the loop when viewed from the east. The Earth’s field here is due north, parallel to the ground, with a strength of . What are the direction and magnitude of the torque on the loop? (b) Does this device have any practical applications as a motor?
Repeat [link] , but with the loop lying flat on the ground with its current circulating counterclockwise (when viewed from above) in a location where the Earth’s field is north, but at an angle below the horizontal and with a strength of .
(a) west
(b) This is not a very significant torque, so practical use would be limited. Also, the current would need to be alternated to make the loop rotate (otherwise it would oscillate).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?