-
Home
- College physics
- Work, energy, and energy resources
- Kinetic energy and the work
Work and energy can reveal distance, too
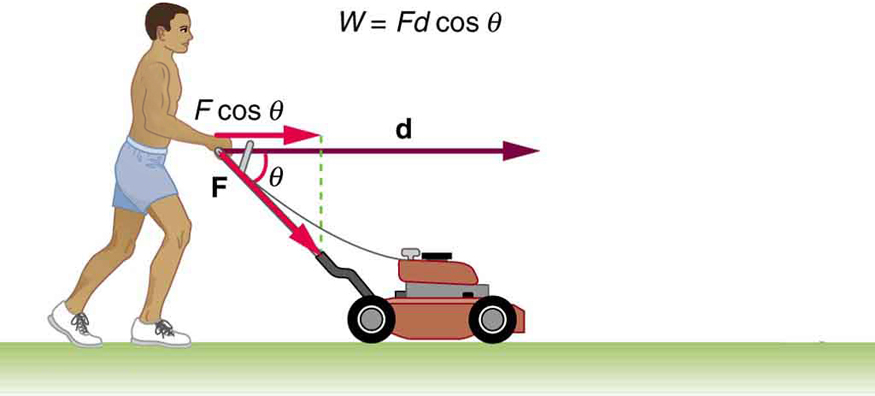
How far does the package in
[link] coast after the push, assuming friction remains constant? Use work and energy considerations.
Strategy
We know that once the person stops pushing, friction will bring the package to rest. In terms of energy, friction does negative work until it has removed all of the package’s kinetic energy. The work done by friction is the force of friction times the distance traveled times the cosine of the angle between the friction force and displacement; hence, this gives us a way of finding the distance traveled after the person stops pushing.
Solution
The normal force and force of gravity cancel in calculating the net force. The horizontal friction force is then the net force, and it acts opposite to the displacement, so
. To reduce the kinetic energy of the package to zero, the work
by friction must be minus the kinetic energy that the package started with plus what the package accumulated due to the pushing. Thus
. Furthermore,
, where
is the distance it takes to stop. Thus,
and so
Discussion
This is a reasonable distance for a package to coast on a relatively friction-free conveyor system. Note that the work done by friction is negative (the force is in the opposite direction of motion), so it removes the kinetic energy.
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Some of the examples in this section can be solved without considering energy, but at the expense of missing out on gaining insights about what work and energy are doing in this situation. On the whole, solutions involving energy are generally shorter and easier than those using kinematics and dynamics alone.
Section summary
- The net work
is the work done by the net force acting on an object.
- Work done on an object transfers energy to the object.
- The translational kinetic energy of an object of mass
moving at speed
is
.
- The work-energy theorem states that the net work
on a system changes its kinetic energy,
.
Conceptual questions
Problems&Exercises
Compare the kinetic energy of a 20,000-kg truck moving at 110 km/h with that of an 80.0-kg astronaut in orbit moving at 27,500 km/h.
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
(a) How fast must a 3000-kg elephant move to have the same kinetic energy as a 65.0-kg sprinter running at 10.0 m/s? (b) Discuss how the larger energies needed for the movement of larger animals would relate to metabolic rates.
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Confirm the value given for the kinetic energy of an aircraft carrier in
[link] . You will need to look up the definition of a nautical mile (1 knot = 1 nautical mile/h).
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
(a) Calculate the force needed to bring a 950-kg car to rest from a speed of 90.0 km/h in a distance of 120 m (a fairly typical distance for a non-panic stop). (b) Suppose instead the car hits a concrete abutment at full speed and is brought to a stop in 2.00 m. Calculate the force exerted on the car and compare it with the force found in part (a).
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
A car’s bumper is designed to withstand a 4.0-km/h (1.1-m/s) collision with an immovable object without damage to the body of the car. The bumper cushions the shock by absorbing the force over a distance. Calculate the magnitude of the average force on a bumper that collapses 0.200 m while bringing a 900-kg car to rest from an initial speed of 1.1 m/s.
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Boxing gloves are padded to lessen the force of a blow. (a) Calculate the force exerted by a boxing glove on an opponent’s face, if the glove and face compress 7.50 cm during a blow in which the 7.00-kg arm and glove are brought to rest from an initial speed of 10.0 m/s. (b) Calculate the force exerted by an identical blow in the gory old days when no gloves were used and the knuckles and face would compress only 2.00 cm. (c) Discuss the magnitude of the force with glove on. Does it seem high enough to cause damage even though it is lower than the force with no glove?
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Using energy considerations, calculate the average force a 60.0-kg sprinter exerts backward on the track to accelerate from 2.00 to 8.00 m/s in a distance of 25.0 m, if he encounters a headwind that exerts an average force of 30.0 N against him.
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Questions & Answers
Three charges q_{1}=+3\mu C, q_{2}=+6\mu C and q_{3}=+8\mu C are located at (2,0)m (0,0)m and (0,3) coordinates respectively. Find the magnitude and direction acted upon q_{2} by the two other charges.Draw the correct graphical illustration of the problem above showing the direction of all forces.
To solve this problem, we need to first find the net force acting on charge q_{2}. The magnitude of the force exerted by q_{1} on q_{2} is given by F=\frac{kq_{1}q_{2}}{r^{2}} where k is the Coulomb constant, q_{1} and q_{2} are the charges of the particles, and r is the distance between them.
Muhammed
What is the direction and net electric force on q_{1}= 5µC located at (0,4)r due to charges q_{2}=7mu located at (0,0)m and q_{3}=3\mu C located at (4,0)m?
what is the change in momentum of a body?
Capacitor is a separation of opposite charges using an insulator of very small dimension between them. Capacitor is used for allowing an AC (alternating current) to pass while a DC (direct current) is blocked.
Gautam
A motor travelling at 72km/m on sighting a stop sign applying the breaks such that under constant deaccelerate in the meters of 50 metres what is the magnitude of the accelerate
What is Thermodynamics
Muordit
velocity can be 72 km/h in question. 72 km/h=20 m/s, v^2=2.a.x , 20^2=2.a.50, a=4 m/s^2.
Mehmet
A boat travels due east at a speed of 40meter per seconds across a river flowing due south at 30meter per seconds. what is the resultant speed of the boat
50 m/s due south east
Someone
which has a higher temperature, 1cup of boiling water or 1teapot of boiling water which can transfer more heat 1cup of boiling water or 1 teapot of boiling water explain your . answer
I believe temperature being an intensive property does not change for any amount of boiling water whereas heat being an extensive property changes with amount/size of the system.
Someone
temperature for any amount of water to boil at ntp is 100⁰C (it is a state function and and intensive property) and it depends both will give same amount of heat because the surface available for heat transfer is greater in case of the kettle as well as the heat stored in it but if you talk.....
Someone
about the amount of heat stored in the system then in that case since the mass of water in the kettle is greater so more energy is required to raise the temperature b/c more molecules of water are present in the kettle
Someone
physics, biology and chemistry
this is my Field
ALIYU
field is a region of space under the influence of some physical properties
Collete
what is ogarnic chemistry
determine the slope giving that 3y+ 2x-14=0
WISDOM
Another formula for Acceleration
pratica A on solution of hydro chloric acid,B is a solution containing 0.5000 mole ofsodium chlorid per dm³,put A in the burret and titrate 20.00 or 25.00cm³ portion of B using melting orange as the indicator. record the deside of your burret tabulate the burret reading and calculate the average volume of acid used?
how do lnternal energy measures
Esrael
Two bodies attract each other electrically. Do they both have to be charged? Answer the same question if the bodies repel one another.
No. According to Isac Newtons law. this two bodies maybe you and the wall beside you.
Attracting depends on the mass och each body and distance between them.
Dlovan
Are you really asking if two bodies have to be charged to be influenced by Coulombs Law?
Robert
like charges repel while unlike charges atttact
Raymond
What is specific heat capacity
Specific heat capacity is a measure of the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of a substance by one degree Celsius (or Kelvin). It is measured in Joules per kilogram per degree Celsius (J/kg°C).
AI-Robot
specific heat capacity is the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of a substance by one degree Celsius or kelvin
ROKEEB
Got questions? Join the online conversation and get instant answers!
Source:
OpenStax, College physics. OpenStax CNX. Jul 27, 2015 Download for free at http://legacy.cnx.org/content/col11406/1.9
Google Play and the Google Play logo are trademarks of Google Inc.