| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
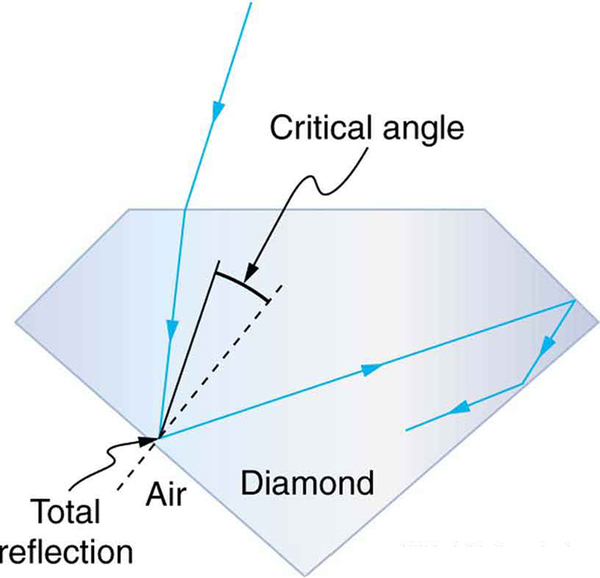
Total internal reflection, coupled with a large index of refraction, explains why diamonds sparkle more than other materials. The critical angle for a diamond-to-air surface is only , and so when light enters a diamond, it has trouble getting back out. (See [link] .) Although light freely enters the diamond, it can exit only if it makes an angle less than . Facets on diamonds are specifically intended to make this unlikely, so that the light can exit only in certain places. Good diamonds are very clear, so that the light makes many internal reflections and is concentrated at the few places it can exit—hence the sparkle. (Zircon is a natural gemstone that has an exceptionally large index of refraction, but not as large as diamond, so it is not as highly prized. Cubic zirconia is manufactured and has an even higher index of refraction ( ), but still less than that of diamond.) The colors you see emerging from a sparkling diamond are not due to the diamond’s color, which is usually nearly colorless. Those colors result from dispersion, the topic of Dispersion: The Rainbow and Prisms . Colored diamonds get their color from structural defects of the crystal lattice and the inclusion of minute quantities of graphite and other materials. The Argyle Mine in Western Australia produces around 90% of the world’s pink, red, champagne, and cognac diamonds, while around 50% of the world’s clear diamonds come from central and southern Africa.
Explore bending of light between two media with different indices of refraction. See how changing from air to water to glass changes the bending angle. Play with prisms of different shapes and make rainbows.

A ring with a colorless gemstone is dropped into water. The gemstone becomes invisible when submerged. Can it be a diamond? Explain.
A high-quality diamond may be quite clear and colorless, transmitting all visible wavelengths with little absorption. Explain how it can sparkle with flashes of brilliant color when illuminated by white light.
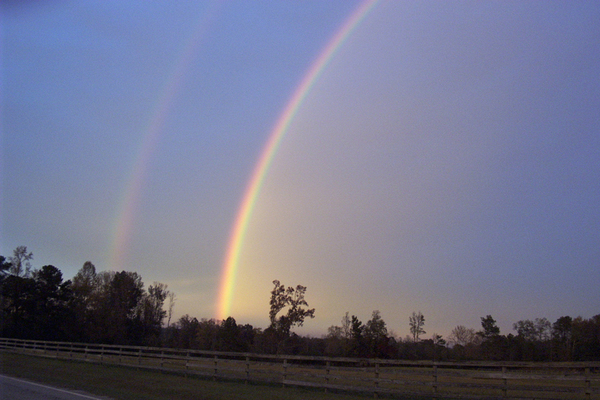
Is it possible that total internal reflection plays a role in rainbows? Explain in terms of indices of refraction and angles, perhaps referring to [link] . Some of us have seen the formation of a double rainbow. Is it physically possible to observe a triple rainbow?

The most common type of mirage is an illusion that light from faraway objects is reflected by a pool of water that is not really there. Mirages are generally observed in deserts, when there is a hot layer of air near the ground. Given that the refractive index of air is lower for air at higher temperatures, explain how mirages can be formed.
Verify that the critical angle for light going from water to air is , as discussed at the end of [link] , regarding the critical angle for light traveling in a polystyrene (a type of plastic) pipe surrounded by air.
(a) At the end of [link] , it was stated that the critical angle for light going from diamond to air is . Verify this. (b) What is the critical angle for light going from zircon to air?
An optical fiber uses flint glass clad with crown glass. What is the critical angle?
At what minimum angle will you get total internal reflection of light traveling in water and reflected from ice?
Suppose you are using total internal reflection to make an efficient corner reflector. If there is air outside and the incident angle is , what must be the minimum index of refraction of the material from which the reflector is made?
You can determine the index of refraction of a substance by determining its critical angle. (a) What is the index of refraction of a substance that has a critical angle of when submerged in water? What is the substance, based on [link] ? (b) What would the critical angle be for this substance in air?
A ray of light, emitted beneath the surface of an unknown liquid with air above it, undergoes total internal reflection as shown in [link] . What is the index of refraction for the liquid and its likely identification?
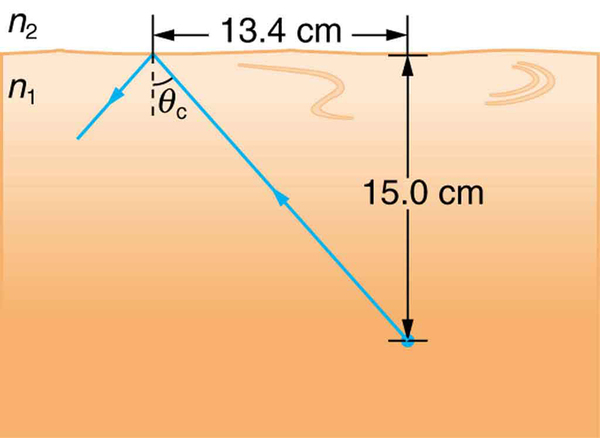
1.50, benzene
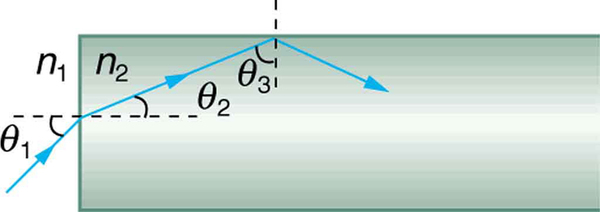
A light ray entering an optical fiber surrounded by air is first refracted and then reflected as shown in [link] . Show that if the fiber is made from crown glass, any incident ray will be totally internally reflected.

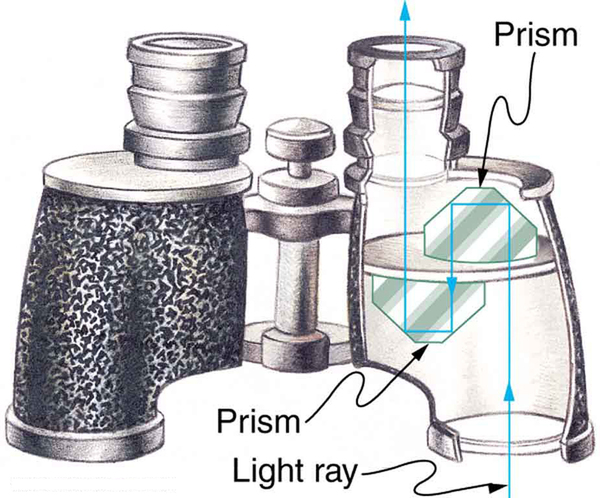
Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?