| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
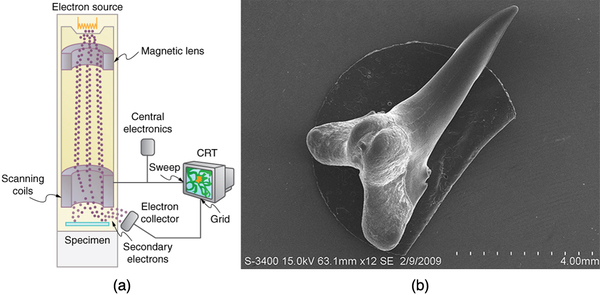
The scanning electron microscope (SEM) provides images by using secondary electrons produced by the primary beam interacting with the surface of the sample (see [link] ). The SEM also uses magnetic lenses to focus the beam onto the sample. However, it moves the beam around electrically to “scan” the sample in the x and y directions. A CCD detector is used to process the data for each electron position, producing images like the one at the beginning of this chapter. The SEM has the advantage of not requiring a thin sample and of providing a 3-D view. However, its resolution is about ten times less than a TEM.
Electrons were the first particles with mass to be directly confirmed to have the wavelength proposed by de Broglie. Subsequently, protons, helium nuclei, neutrons, and many others have been observed to exhibit interference when they interact with objects having sizes similar to their de Broglie wavelength. The de Broglie wavelength for massless particles was well established in the 1920s for photons, and it has since been observed that all massless particles have a de Broglie wavelength The wave nature of all particles is a universal characteristic of nature. We shall see in following sections that implications of the de Broglie wavelength include the quantization of energy in atoms and molecules, and an alteration of our basic view of nature on the microscopic scale. The next section, for example, shows that there are limits to the precision with which we may make predictions, regardless of how hard we try. There are even limits to the precision with which we may measure an object’s location or energy.
The wave nature of matter allows it to exhibit all the characteristics of other, more familiar, waves. Diffraction gratings, for example, produce diffraction patterns for light that depend on grating spacing and the wavelength of the light. This effect, as with most wave phenomena, is most pronounced when the wave interacts with objects having a size similar to its wavelength. For gratings, this is the spacing between multiple slits.) When electrons interact with a system having a spacing similar to the electron wavelength, they show the same types of interference patterns as light does for diffraction gratings, as shown at top left in [link] .
Atoms are spaced at regular intervals in a crystal as parallel planes, as shown in the bottom part of [link] . The spacings between these planes act like the openings in a diffraction grating. At certain incident angles, the paths of electrons scattering from successive planes differ by one wavelength and, thus, interfere constructively. At other angles, the path length differences are not an integral wavelength, and there is partial to total destructive interference. This type of scattering from a large crystal with well-defined lattice planes can produce dramatic interference patterns. It is called Bragg reflection , for the father-and-son team who first explored and analyzed it in some detail. The expanded view also shows the path-length differences and indicates how these depend on incident angle in a manner similar to the diffraction patterns for x rays reflecting from a crystal.
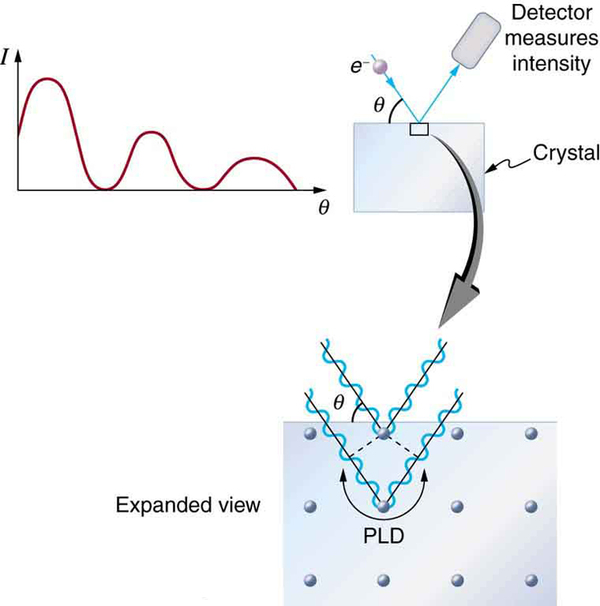
Let us take the spacing between parallel planes of atoms in the crystal to be . As mentioned, if the path length difference (PLD) for the electrons is a whole number of wavelengths, there will be constructive interference—that is, . Because we have constructive interference when This relationship is called the Bragg equation and applies not only to electrons but also to x rays.
The wavelength of matter is a submicroscopic characteristic that explains a macroscopic phenomenon such as Bragg reflection. Similarly, the wavelength of light is a submicroscopic characteristic that explains the macroscopic phenomenon of diffraction patterns.
How does the interference of water waves differ from the interference of electrons? How are they analogous?
Describe one type of evidence for the wave nature of matter.
Describe one type of evidence for the particle nature of EM radiation.
At what velocity will an electron have a wavelength of 1.00 m?
What is the wavelength of an electron moving at 3.00% of the speed of light?
At what velocity does a proton have a 6.00-fm wavelength (about the size of a nucleus)? Assume the proton is nonrelativistic. (1 femtometer = )
What is the velocity of a 0.400-kg billiard ball if its wavelength is 7.50 cm (large enough for it to interfere with other billiard balls)?
Find the wavelength of a proton moving at 1.00% of the speed of light.
Experiments are performed with ultracold neutrons having velocities as small as 1.00 m/s. (a) What is the wavelength of such a neutron? (b) What is its kinetic energy in eV?
(a) Find the velocity of a neutron that has a 6.00-fm wavelength (about the size of a nucleus). Assume the neutron is nonrelativistic. (b) What is the neutron’s kinetic energy in MeV?
(a)
(b)
What is the wavelength of an electron accelerated through a 30.0-kV potential, as in a TV tube?
What is the kinetic energy of an electron in a TEM having a 0.0100-nm wavelength?
(a) Calculate the velocity of an electron that has a wavelength of (b) Through what voltage must the electron be accelerated to have this velocity?
The velocity of a proton emerging from a Van de Graaff accelerator is 25.0% of the speed of light. (a) What is the proton’s wavelength? (b) What is its kinetic energy, assuming it is nonrelativistic? (c) What was the equivalent voltage through which it was accelerated?
(a) 5.29 fm
(b)
(c) 29.4 MV
The kinetic energy of an electron accelerated in an x-ray tube is 100 keV. Assuming it is nonrelativistic, what is its wavelength?
Unreasonable Results
(a) Assuming it is nonrelativistic, calculate the velocity of an electron with a 0.100-fm wavelength (small enough to detect details of a nucleus). (b) What is unreasonable about this result? (c) Which assumptions are unreasonable or inconsistent?
(a)
(b) This is thousands of times the speed of light (an impossibility).
(c) The assumption that the electron is non-relativistic is unreasonable at this wavelength.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?