| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
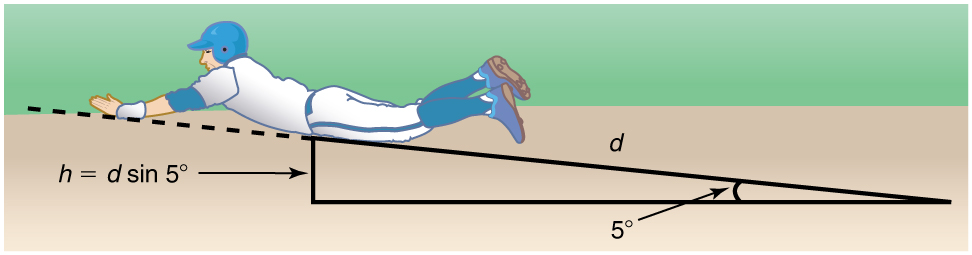
Suppose that the player from [link] is running up a hill having a incline upward with a surface similar to that in the baseball stadium. The player slides with the same initial speed. Determine how far he slides.
Strategy
In this case, the work done by the nonconservative friction force on the player reduces the mechanical energy he has from his kinetic energy at zero height, to the final mechanical energy he has by moving through distance to reach height along the hill, with . This is expressed by the equation
Solution
The work done by friction is again ; initially the potential energy is and the kinetic energy is ; the final energy contributions are for the kinetic energy and for the potential energy.
Substituting these values gives
Solve this for to obtain
Discussion
As might have been expected, the player slides a shorter distance by sliding uphill. Note that the problem could also have been solved in terms of the forces directly and the work energy theorem, instead of using the potential energy. This method would have required combining the normal force and force of gravity vectors, which no longer cancel each other because they point in different directions, and friction, to find the net force. You could then use the net force and the net work to find the distance that reduces the kinetic energy to zero. By applying conservation of energy and using the potential energy instead, we need only consider the gravitational potential energy , without combining and resolving force vectors. This simplifies the solution considerably.
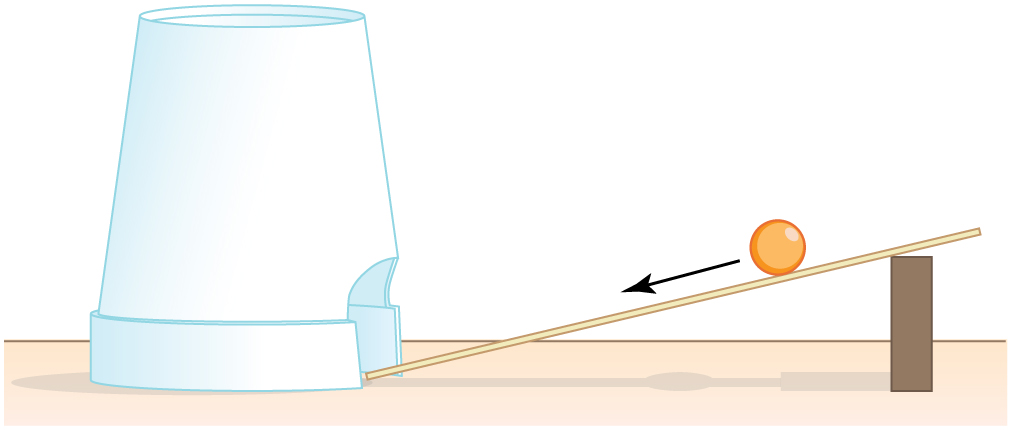
This experiment involves the conversion of gravitational potential energy into thermal energy. Use the ruler, book, and marble from Take-Home Investigation—Converting Potential to Kinetic Energy . In addition, you will need a foam cup with a small hole in the side, as shown in [link] . From the 10-cm position on the ruler, let the marble roll into the cup positioned at the bottom of the ruler. Measure the distance the cup moves before stopping. What forces caused it to stop? What happened to the kinetic energy of the marble at the bottom of the ruler? Next, place the marble at the 20-cm and the 30-cm positions and again measure the distance the cup moves after the marble enters it. Plot the distance the cup moves versus the initial marble position on the ruler. Is this relationship linear?
With some simple assumptions, you can use these data to find the coefficient of kinetic friction of the cup on the table. The force of friction on the cup is , where the normal force is just the weight of the cup plus the marble. The normal force and force of gravity do no work because they are perpendicular to the displacement of the cup, which moves horizontally. The work done by friction is . You will need the mass of the marble as well to calculate its initial kinetic energy.
It is interesting to do the above experiment also with a steel marble (or ball bearing). Releasing it from the same positions on the ruler as you did with the glass marble, is the velocity of this steel marble the same as the velocity of the marble at the bottom of the ruler? Is the distance the cup moves proportional to the mass of the steel and glass marbles?
Explore forces, energy and work as you push household objects up and down a ramp. Lower and raise the ramp to see how the angle of inclination affects the parallel forces acting on the file cabinet. Graphs show forces, energy and work.

A 60.0-kg skier with an initial speed of 12.0 m/s coasts up a 2.50-m-high rise as shown in [link] . Find her final speed at the top, given that the coefficient of friction between her skis and the snow is 0.0800. (Hint: Find the distance traveled up the incline assuming a straight-line path as shown in the figure.)
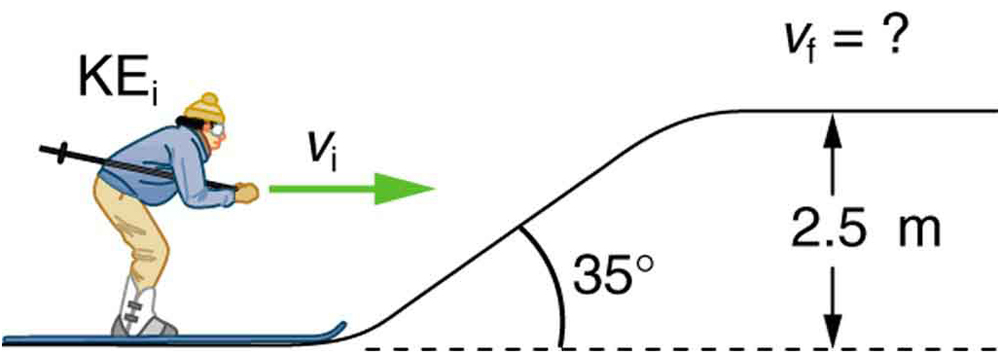
9.46 m/s
(a) How high a hill can a car coast up (engine disengaged) if work done by friction is negligible and its initial speed is 110 km/h? (b) If, in actuality, a 750-kg car with an initial speed of 110 km/h is observed to coast up a hill to a height 22.0 m above its starting point, how much thermal energy was generated by friction? (c) What is the average force of friction if the hill has a slope above the horizontal?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?