| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
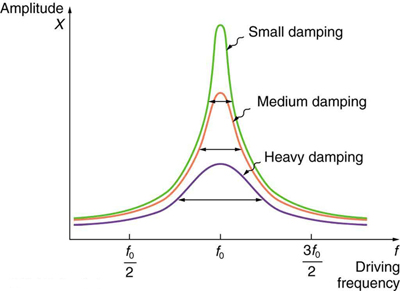
It is interesting that the widths of the resonance curves shown in [link] depend on damping: the less the damping, the narrower the resonance. The message is that if you want a driven oscillator to resonate at a very specific frequency, you need as little damping as possible. Little damping is the case for piano strings and many other musical instruments. Conversely, if you want small-amplitude oscillations, such as in a car’s suspension system, then you want heavy damping. Heavy damping reduces the amplitude, but the tradeoff is that the system responds at more frequencies.
These features of driven harmonic oscillators apply to a huge variety of systems. When you tune a radio, for example, you are adjusting its resonant frequency so that it only oscillates to the desired station’s broadcast (driving) frequency. The more selective the radio is in discriminating between stations, the smaller its damping. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a widely used medical diagnostic tool in which atomic nuclei (mostly hydrogen nuclei) are made to resonate by incoming radio waves (on the order of 100 MHz). A child on a swing is driven by a parent at the swing’s natural frequency to achieve maximum amplitude. In all of these cases, the efficiency of energy transfer from the driving force into the oscillator is best at resonance. Speed bumps and gravel roads prove that even a car’s suspension system is not immune to resonance. In spite of finely engineered shock absorbers, which ordinarily convert mechanical energy to thermal energy almost as fast as it comes in, speed bumps still cause a large-amplitude oscillation. On gravel roads that are corrugated, you may have noticed that if you travel at the “wrong” speed, the bumps are very noticeable whereas at other speeds you may hardly feel the bumps at all. [link] shows a photograph of a famous example (the Tacoma Narrows Bridge) of the destructive effects of a driven harmonic oscillation. The Millennium Bridge in London was closed for a short period of time for the same reason while inspections were carried out.
In our bodies, the chest cavity is a clear example of a system at resonance. The diaphragm and chest wall drive the oscillations of the chest cavity which result in the lungs inflating and deflating. The system is critically damped and the muscular diaphragm oscillates at the resonant value for the system, making it highly efficient.

A famous magic trick involves a performer singing a note toward a crystal glass until the glass shatters. Explain why the trick works in terms of resonance and natural frequency.
The performer must be singing a note that corresponds to the natural frequency of the glass. As the sound wave is directed at the glass, the glass responds by resonating at the same frequency as the sound wave. With enough energy introduced into the system, the glass begins to vibrate and eventually shatters.
Why are soldiers in general ordered to “route step” (walk out of step) across a bridge?
How much energy must the shock absorbers of a 1200-kg car dissipate in order to damp a bounce that initially has a velocity of 0.800 m/s at the equilibrium position? Assume the car returns to its original vertical position.
384 J
If a car has a suspension system with a force constant of , how much energy must the car’s shocks remove to dampen an oscillation starting with a maximum displacement of 0.0750 m?
(a) How much will a spring that has a force constant of 40.0 N/m be stretched by an object with a mass of 0.500 kg when hung motionless from the spring? (b) Calculate the decrease in gravitational potential energy of the 0.500-kg object when it descends this distance. (c) Part of this gravitational energy goes into the spring. Calculate the energy stored in the spring by this stretch, and compare it with the gravitational potential energy. Explain where the rest of the energy might go.
(a). 0.123 m
(b). −0.600 J
(c). 0.300 J. The rest of the energy may go into heat caused by friction and other damping forces.
Suppose you have a 0.750-kg object on a horizontal surface connected to a spring that has a force constant of 150 N/m. There is simple friction between the object and surface with a static coefficient of friction . (a) How far can the spring be stretched without moving the mass? (b) If the object is set into oscillation with an amplitude twice the distance found in part (a), and the kinetic coefficient of friction is , what total distance does it travel before stopping? Assume it starts at the maximum amplitude.
Engineering Application: A suspension bridge oscillates with an effective force constant of . (a) How much energy is needed to make it oscillate with an amplitude of 0.100 m? (b) If soldiers march across the bridge with a cadence equal to the bridge’s natural frequency and impart of energy each second, how long does it take for the bridge’s oscillations to go from 0.100 m to 0.500 m amplitude?
(a)
(b) s

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?