| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

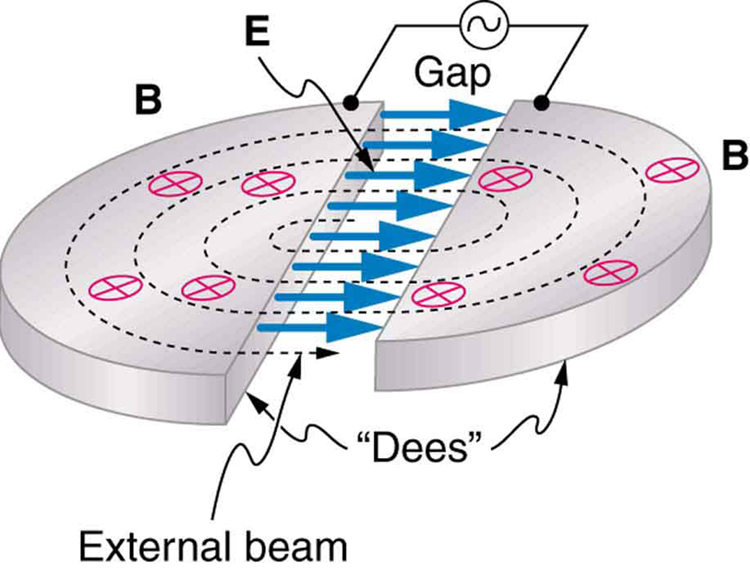
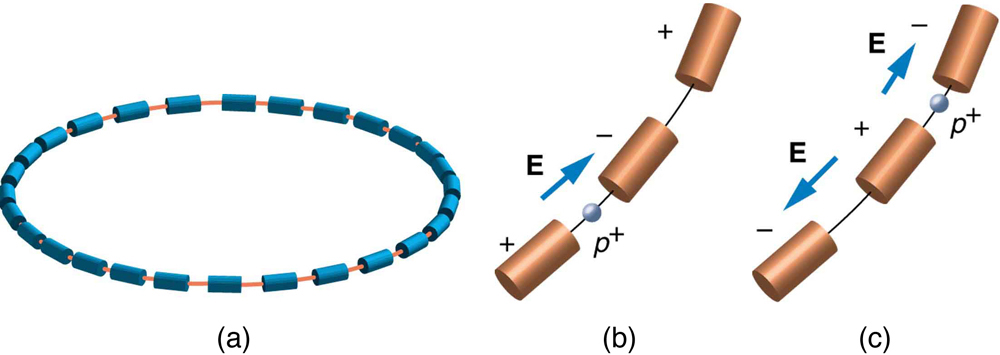
Physicists have built ever-larger machines, first to reduce the wavelength of the probe and obtain greater detail, then to put greater energy into collisions to create new particles. Each major energy increase brought new information, sometimes producing spectacular progress, motivating the next step. One major innovation was driven by the desire to create more massive particles. Since momentum needs to be conserved in a collision, the particles created by a beam hitting a stationary target should recoil. This means that part of the energy input goes into recoil kinetic energy, significantly limiting the fraction of the beam energy that can be converted into new particles. One solution to this problem is to have head-on collisions between particles moving in opposite directions. Colliding beams are made to meet head-on at points where massive detectors are located. Since the total incoming momentum is zero, it is possible to create particles with momenta and kinetic energies near zero. Particles with masses equivalent to twice the beam energy can thus be created. Another innovation is to create the antimatter counterpart of the beam particle, which thus has the opposite charge and circulates in the opposite direction in the same beam pipe. For a schematic representation, see [link] .
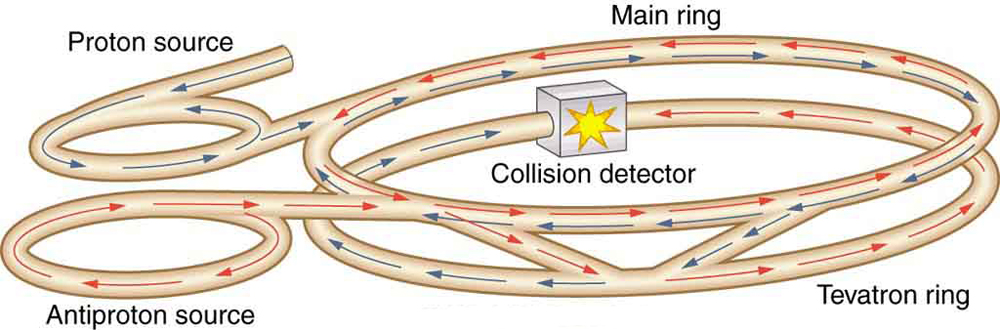
Detectors capable of finding the new particles in the spray of material that emerges from colliding beams are as impressive as the accelerators. While the Fermilab Tevatron had proton and antiproton beam energies of about 1 TeV, so that it can create particles up to , the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at the European Center for Nuclear Research (CERN) has achieved beam energies of 3.5 TeV, so that it has a 7-TeV collision energy; CERN hopes to double the beam energy in 2014. The now-canceled Superconducting Super Collider was being constructed in Texas with a design energy of 20 TeV to give a 40-TeV collision energy. It was to be an oval 30 km in diameter. Its cost as well as the politics of international research funding led to its demise.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?