| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
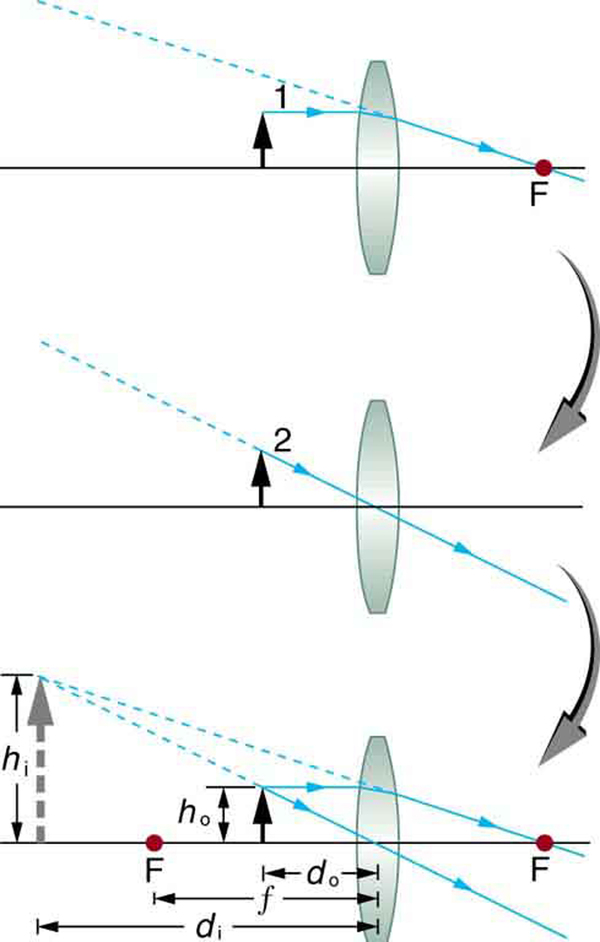
An image that is on the same side of the lens as the object and cannot be projected on a screen is called a virtual image.
Suppose the book page in [link] (a) is held 7.50 cm from a convex lens of focal length 10.0 cm, such as a typical magnifying glass might have. What magnification is produced?
Strategy and Concept
We are given that and , so we have a situation where the object is placed closer to the lens than its focal length. We therefore expect to get a case 2 virtual image with a positive magnification that is greater than 1. Ray tracing produces an image like that shown in [link] , but we will use the thin lens equations to get numerical solutions in this example.
Solution
To find the magnification , we try to use magnification equation, . We do not have a value for , so that we must first find the location of the image using lens equation. (The procedure is the same as followed in the preceding example, where and were known.) Rearranging the magnification equation to isolate gives
Entering known values, we obtain a value for :
This must be inverted to find :
Now the thin lens equation can be used to find the magnification , since both and are known. Entering their values gives
Discussion
A number of results in this example are true of all case 2 images, as well as being consistent with [link] . Magnification is indeed positive (as predicted), meaning the image is upright. The magnification is also greater than 1, meaning that the image is larger than the object—in this case, by a factor of 4. Note that the image distance is negative. This means the image is on the same side of the lens as the object. Thus the image cannot be projected and is virtual. (Negative values of occur for virtual images.) The image is farther from the lens than the object, since the image distance is greater in magnitude than the object distance. The location of the image is not obvious when you look through a magnifier. In fact, since the image is bigger than the object, you may think the image is closer than the object. But the image is farther away, a fact that is useful in correcting farsightedness, as we shall see in a later section.
A third type of image is formed by a diverging or concave lens. Try looking through eyeglasses meant to correct nearsightedness. (See [link] .) You will see an image that is upright but smaller than the object. This means that the magnification is positive but less than 1. The ray diagram in [link] shows that the image is on the same side of the lens as the object and, hence, cannot be projected—it is a virtual image. Note that the image is closer to the lens than the object. This is a case 3 image, formed for any object by a negative focal length or diverging lens.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?