| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
No charge is actually created or destroyed when charges are separated as we have been discussing. Rather, existing charges are moved about. In fact, in all situations the total amount of charge is always constant. This universally obeyed law of nature is called the law of conservation of charge .
Total charge is constant in any process.
In more exotic situations, such as in particle accelerators, mass, , can be created from energy in the amount . Sometimes, the created mass is charged, such as when an electron is created. Whenever a charged particle is created, another having an opposite charge is always created along with it, so that the total charge created is zero. Usually, the two particles are “matter-antimatter” counterparts. For example, an antielectron would usually be created at the same time as an electron. The antielectron has a positive charge (it is called a positron), and so the total charge created is zero. (See [link] .) All particles have antimatter counterparts with opposite signs. When matter and antimatter counterparts are brought together, they completely annihilate one another. By annihilate, we mean that the mass of the two particles is converted to energy E , again obeying the relationship . Since the two particles have equal and opposite charge, the total charge is zero before and after the annihilation; thus, total charge is conserved.
Only a limited number of physical quantities are universally conserved. Charge is one—energy, momentum, and angular momentum are others. Because they are conserved, these physical quantities are used to explain more phenomena and form more connections than other, less basic quantities. We find that conserved quantities give us great insight into the rules followed by nature and hints to the organization of nature. Discoveries of conservation laws have led to further discoveries, such as the weak nuclear force and the quark substructure of protons and other particles.
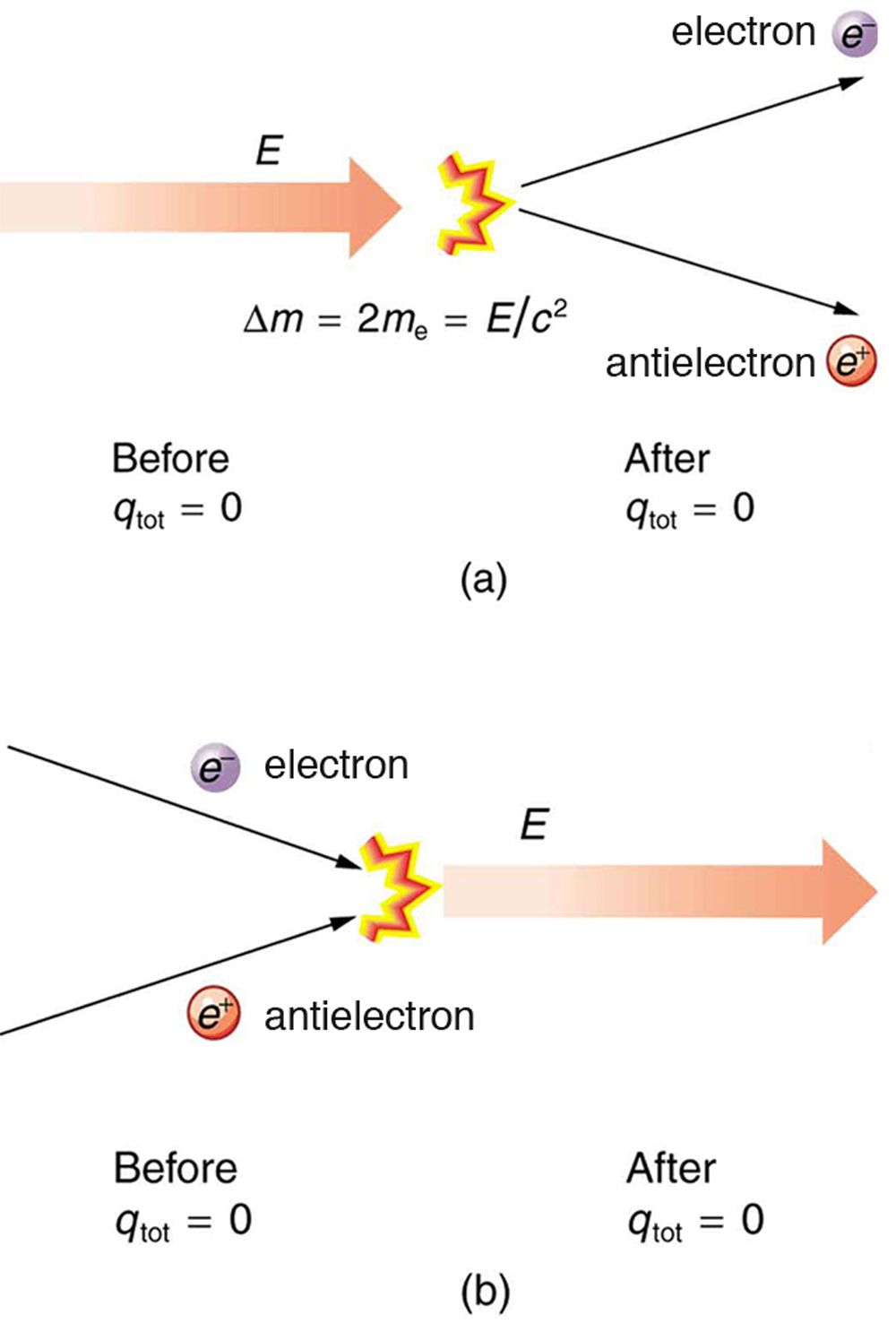
The law of conservation of charge is absolute—it has never been observed to be violated. Charge, then, is a special physical quantity, joining a very short list of other quantities in nature that are always conserved. Other conserved quantities include energy, momentum, and angular momentum.
Why does a balloon stick to your sweater? Rub a balloon on a sweater, then let go of the balloon and it flies over and sticks to the sweater. View the charges in the sweater, balloons, and the wall.

There are very large numbers of charged particles in most objects. Why, then, don’t most objects exhibit static electricity?
Why do most objects tend to contain nearly equal numbers of positive and negative charges?
Common static electricity involves charges ranging from nanocoulombs to microcoulombs. (a) How many electrons are needed to form a charge of (b) How many electrons must be removed from a neutral object to leave a net charge of ?
(a)
(b)
If electrons move through a pocket calculator during a full day’s operation, how many coulombs of charge moved through it?
To start a car engine, the car battery moves electrons through the starter motor. How many coulombs of charge were moved?
-600 C
A certain lightning bolt moves 40.0 C of charge. How many fundamental units of charge is this?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?