| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
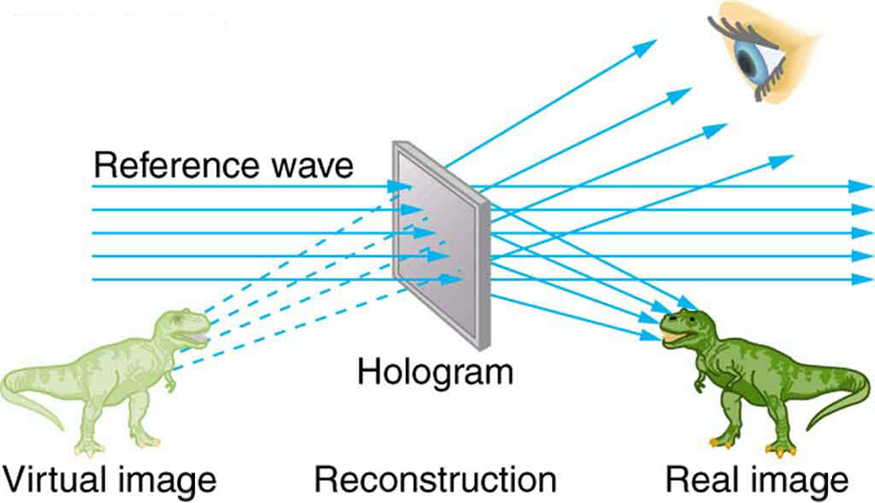
The hologram illustrated in [link] is a transmission hologram. Holograms that are viewed with reflected light, such as the white light holograms on credit cards, are reflection holograms and are more common. White light holograms often appear a little blurry with rainbow edges, because the diffraction patterns of various colors of light are at slightly different locations due to their different wavelengths. Further uses of holography include all types of 3-D information storage, such as of statues in museums and engineering studies of structures and 3-D images of human organs. Invented in the late 1940s by Dennis Gabor (1900–1970), who won the 1971 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work, holography became far more practical with the development of the laser. Since lasers produce coherent single-wavelength light, their interference patterns are more pronounced. The precision is so great that it is even possible to record numerous holograms on a single piece of film by just changing the angle of the film for each successive image. This is how the holograms that move as you walk by them are produced—a kind of lensless movie.
In a similar way, in the medical field, holograms have allowed complete 3-D holographic displays of objects from a stack of images. Storing these images for future use is relatively easy. With the use of an endoscope, high-resolution 3-D holographic images of internal organs and tissues can be made.
How do the allowed orbits for electrons in atoms differ from the allowed orbits for planets around the sun? Explain how the correspondence principle applies here.
Atomic and molecular spectra are discrete. What does discrete mean, and how are discrete spectra related to the quantization of energy and electron orbits in atoms and molecules?
Hydrogen gas can only absorb EM radiation that has an energy corresponding to a transition in the atom, just as it can only emit these discrete energies. When a spectrum is taken of the solar corona, in which a broad range of EM wavelengths are passed through very hot hydrogen gas, the absorption spectrum shows all the features of the emission spectrum. But when such EM radiation passes through room-temperature hydrogen gas, only the Lyman series is absorbed. Explain the difference.
Lasers are used to burn and read CDs. Explain why a laser that emits blue light would be capable of burning and reading more information than one that emits infrared.
The coating on the inside of fluorescent light tubes absorbs ultraviolet light and subsequently emits visible light. An inventor claims that he is able to do the reverse process. Is the inventor’s claim possible?
What is the difference between fluorescence and phosphorescence?
How can you tell that a hologram is a true three-dimensional image and that those in 3-D movies are not?
[link] shows the energy-level diagram for neon. (a) Verify that the energy of the photon emitted when neon goes from its metastable state to the one immediately below is equal to 1.96 eV. (b) Show that the wavelength of this radiation is 633 nm. (c) What wavelength is emitted when the neon makes a direct transition to its ground state?
(a) 1.96 eV
(b)
(c) 60.0 nm
A helium-neon laser is pumped by electric discharge. What wavelength electromagnetic radiation would be needed to pump it? See [link] for energy-level information.
Ruby lasers have chromium atoms doped in an aluminum oxide crystal. The energy level diagram for chromium in a ruby is shown in [link] . What wavelength is emitted by a ruby laser?

693 nm
(a) What energy photons can pump chromium atoms in a ruby laser from the ground state to its second and third excited states? (b) What are the wavelengths of these photons? Verify that they are in the visible part of the spectrum.
Some of the most powerful lasers are based on the energy levels of neodymium in solids, such as glass, as shown in [link] . (a) What average wavelength light can pump the neodymium into the levels above its metastable state? (b) Verify that the 1.17 eV transition produces radiation.
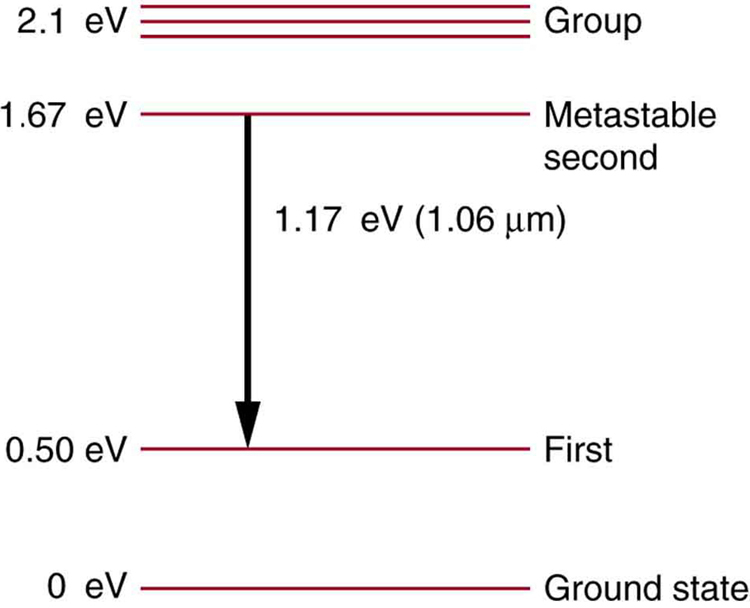
(a) 590 nm
(b)

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?