| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

Following ideas remarkably similar to those of the ancient Greeks, we continue to look for smaller and smaller structures in nature, hoping ultimately to find and understand the most fundamental building blocks that exist. Atomic physics deals with the smallest units of elements and compounds. In its study, we have found a relatively small number of atoms with systematic properties that explained a tremendous range of phenomena. Nuclear physics is concerned with the nuclei of atoms and their substructures. Here, a smaller number of components—the proton and neutron—make up all nuclei. Exploring the systematic behavior of their interactions has revealed even more about matter, forces, and energy. Particle physics deals with the substructures of atoms and nuclei and is particularly aimed at finding those truly fundamental particles that have no further substructure. Just as in atomic and nuclear physics, we have found a complex array of particles and properties with systematic characteristics analogous to the periodic table and the chart of nuclides. An underlying structure is apparent, and there is some reason to think that we are finding particles that have no substructure. Of course, we have been in similar situations before. For example, atoms were once thought to be the ultimate substructure. Perhaps we will find deeper and deeper structures and never come to an ultimate substructure. We may never really know, as indicated in [link] .
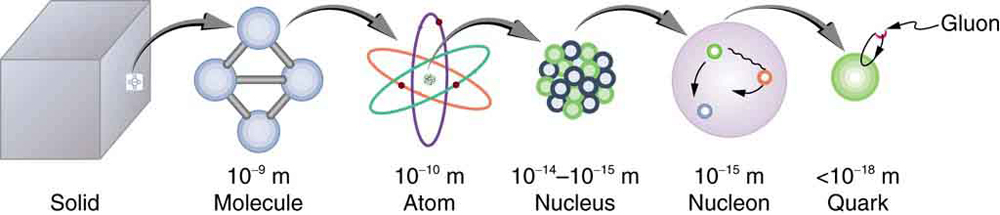
This chapter covers the basics of particle physics as we know it today. An amazing convergence of topics is evolving in particle physics. We find that some particles are intimately related to forces, and that nature on the smallest scale may have its greatest influence on the large-scale character of the universe. It is an adventure exceeding the best science fiction because it is not only fantastic, it is real.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?