| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In Kinematics , we studied motion along a straight line and introduced such concepts as displacement, velocity, and acceleration. Two-Dimensional Kinematics dealt with motion in two dimensions. Projectile motion is a special case of two-dimensional kinematics in which the object is projected into the air, while being subject to the gravitational force, and lands a distance away. In this chapter, we consider situations where the object does not land but moves in a curve. We begin the study of uniform circular motion by defining two angular quantities needed to describe rotational motion.
When objects rotate about some axis—for example, when the CD (compact disc) in [link] rotates about its center—each point in the object follows a circular arc. Consider a line from the center of the CD to its edge. Each pit used to record sound along this line moves through the same angle in the same amount of time. The rotation angle is the amount of rotation and is analogous to linear distance. We define the rotation angle to be the ratio of the arc length to the radius of curvature:
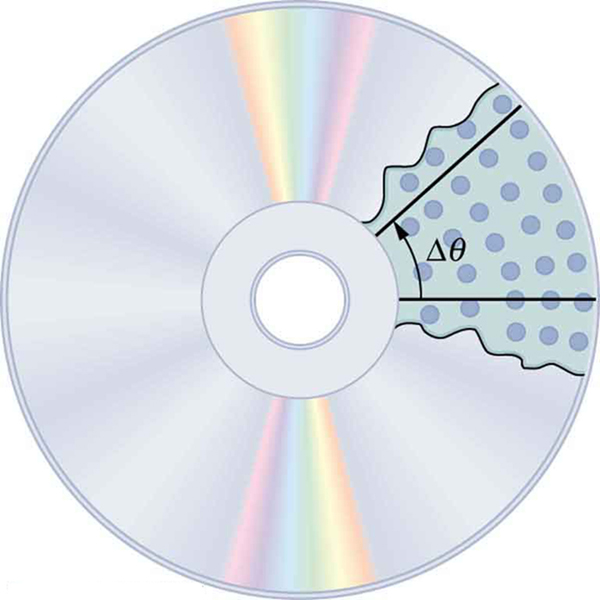
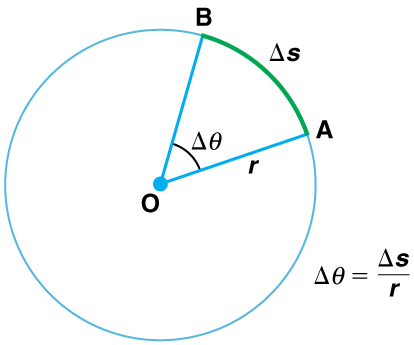
The arc length is the distance traveled along a circular path as shown in [link] Note that is the radius of curvature of the circular path.
We know that for one complete revolution, the arc length is the circumference of a circle of radius . The circumference of a circle is . Thus for one complete revolution the rotation angle is
This result is the basis for defining the units used to measure rotation angles, to be radians (rad), defined so that
A comparison of some useful angles expressed in both degrees and radians is shown in [link] .
| Degree Measures | Radian Measure |
|---|---|
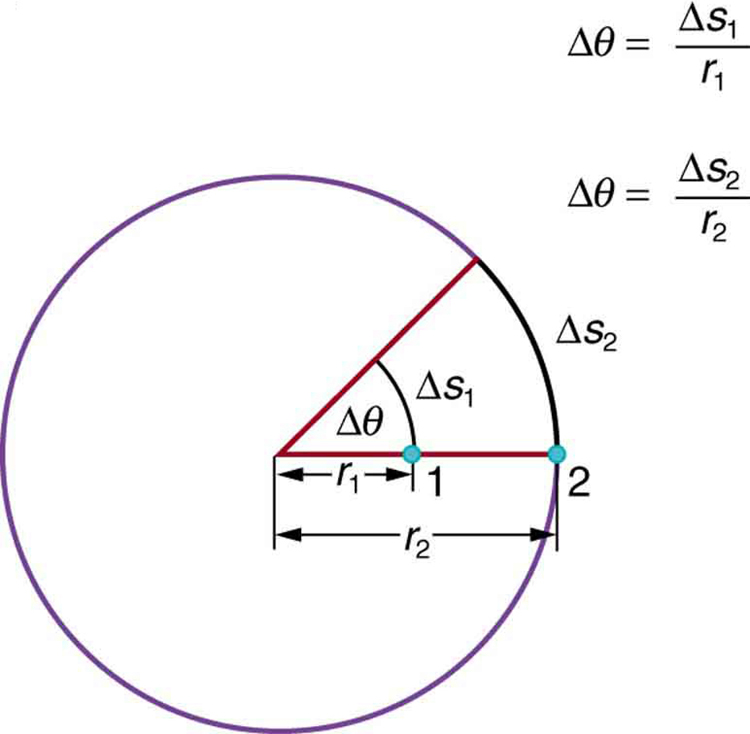
If rad, then the CD has made one complete revolution, and every point on the CD is back at its original position. Because there are in a circle or one revolution, the relationship between radians and degrees is thus
so that
How fast is an object rotating? We define angular velocity as the rate of change of an angle. In symbols, this is
where an angular rotation takes place in a time . The greater the rotation angle in a given amount of time, the greater the angular velocity. The units for angular velocity are radians per second (rad/s).
Angular velocity is analogous to linear velocity . To get the precise relationship between angular and linear velocity, we again consider a pit on the rotating CD. This pit moves an arc length in a time , and so it has a linear velocity

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?